Learning curves for robotic pancreatic surgery-from distal pancreatectomy to pancreaticoduodenectomy
- PMID: 30407289
- PMCID: PMC6250552
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013000
Learning curves for robotic pancreatic surgery-from distal pancreatectomy to pancreaticoduodenectomy
Abstract
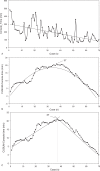
This study sought to identify the learning curves of console time (CT) for robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy (RPD) and robotic distal pancreatectomy (RDP). Perioperative outcomes were compared between the early group of surgeries performed early in the learning curve and the late group of surgeries performed after the learning curve.Pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) is a technically demanding and challenging procedure carrying a high morbidity.Data for RDP and RPD were prospectively collected for analysis. The learning curve was assessed by cumulative sum (CUSUM). Based on CUSUM analyses, patients were divided into the early group and the late group.There were 70 RDP and 61 RPD cases. It required 37 cases to overcome the learning curve for RDP and 20 cases for RPD. The median console time was significantly shorter in the late group for both RDP (112 minutes vs 225 minutes, P < .001) and RPD (360 minuntes vs 520 minutes, P < .001). Median blood loss was significantly less in the late group for both RDP (30 cc vs 100 cc, P = .003) and RPD (100 cc vs 200 cc, P < .001). No surgical mortality occurred in either group. Clinically relevant pancreatic fistula rate was 22.9% for RDP (32.4% in the early group vs 12.1% in the late group, P = .043), and 11.5% for RPD (0 in early group vs 17.1% in late group, P = .084).This study demonstrates that the RPD learning curve is 20 cases with prior experience of RDP and confirms the safety and feasibility of both RPD and RDP. Practice and familiarity with the robotic platform are likely to contribute to significant shortening of the learning curve in robotic pancreatic surgery, while knowledge and experience, in addition to practical skills, are also essential to minimize the potential surgical risks of RPD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Boggi U, Signori S, De Lio N, et al. Feasibility of robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy. Br J Surg 2013;100:917–25. - PubMed
-
- Napoli N, Kauffmann EF, Menonna F, et al. Indications, technique, and results of robotic pancreatoduodenectomy. Updates Surg 2016;68:295–305. - PubMed
-
- Napoli N, Kauffmann EF, Palmeri M, et al. The learning curve in robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy. Dig Surg 2016;33:299–307. - PubMed
-
- Stafford AT, Walsh RM. Robotic surgery of the pancreas: the current state of the art. J Surg Oncol 2015;112:289–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

