Discovery of Vilaprisan (BAY 1002670): A Highly Potent and Selective Progesterone Receptor Modulator Optimized for Gynecologic Therapies
- PMID: 30407750
- PMCID: PMC6282584
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201800487
Discovery of Vilaprisan (BAY 1002670): A Highly Potent and Selective Progesterone Receptor Modulator Optimized for Gynecologic Therapies
Abstract
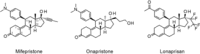
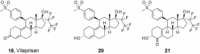
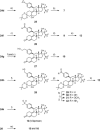
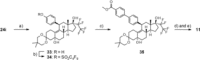
Progesterone plays an important role in the female reproductive system. However, there is also evidence that gynecologic disorders/diseases such as uterine fibroids and endometriosis are progesterone-dependent. Steroidal and non-steroidal selective progesterone receptor modulators (SPRMs) have shown potential for the treatment of such diseases. Steroidal SPRMs, including mifepristone and ulipristal acetate, have proven effective in clinical trials. However, several steroidal SPRMs containing a dimethylamino substituent have been associated with elevated liver enzymes in patients. An earlier drug discovery program identified lonaprisan as a highly selective SPRM that did not show drug-related change in liver enzyme activity. Building on data obtained from that work, here we describe the research program that culminated in the discovery of a novel steroidal SPRM, vilaprisan, which combines an extremely high potency with very favorable drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic properties. Vilaprisan has entered clinical development and is currently undergoing phase 3 clinical trials.
Keywords: fluorinated ligands; gynecologic therapies; methyl sulfone; selective progesterone receptor modulator; structure-activity relationships.
© 2018 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

References
-
- Möller C., Hoffmann J., Kirkland T. A., Schwede W., Expert Opin. Invest. Drugs 2008, 17, 469–479. - PubMed
-
- Bélanger A., Philibert D., Teutsch G., Steroids 1981, 37, 361–382. - PubMed
-
- None
-
- Han S. J., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O′Malley B., Endocrinology 2007, 148, 2471–2486; - PubMed
-
- Afhüppe W., Sommer A., Müller J., Schwede W., Fuhrmann U., Möller C., J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 113, 105–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

