Associations between three XRCC1 polymorphisms and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis of case-control studies
- PMID: 30408066
- PMCID: PMC6226104
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206853
Associations between three XRCC1 polymorphisms and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis of case-control studies
Abstract
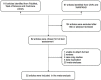
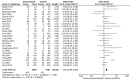
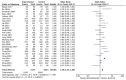
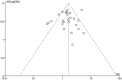
Conflicting results have been obtained regarding the association between X-ray repair cross complementation group 1 (XRCC1) and susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this study, associations between HCC and three polymorphisms (Arg194Trp, Arg280His, and Arg399Gln) were evaluated using a meta-analysis approach. PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, the Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, and the Wanfang standard database were systematically searched to identify all relevant case-control studies published through March 2018. A total of 32 case-control studies, including 13 that evaluated Arg194Trp, 14 that evaluated Arg280His, and 26 that evaluated Arg399Gln, were analyzed. In the entire study population, XRCC1 Arg399Gln was significantly associated not only with overall risk of HCC (homozygous model, OR = 1.61, 95% CI: 1.40-1.85, P < 0.05; recessive model, OR = 1.40, 95% CI: 1.23-1.59, P < 0.05) but also with the risk of HCC in Chinese patients (homozygous model, OR = 1.78, 95% CI: 1.53-2.08, P < 0.05; recessive model, OR = 1.47, 95% CI: 1.27-1.70, P < 0.05). Limiting the analysis to studies demonstrating Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE), the results were consistent and robust. Similarly, a significant association between XRCC1 Arg399Gln and HCC risk was found in healthy controls in the general population but not in hospital controls. Trial sequential analysis (TSA), false-positive report probabilities (FPRP), and combined genotype analysis revealed that XRCC1 Arg399Gln is mainly associated with susceptibility to liver cancer. However, there was no association between Arg194Trp or Arg280His and the risk of HCC. These results, indicating that the Arg399Gln polymorphism of XRCC1 is associated with the risk of HCC in the Chinese population, provide a basis for the development of improved detection and treatment approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

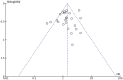
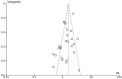
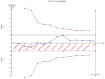
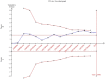
Similar articles
-
X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 polymorphisms and hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug 21;18(31):4207-14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4207. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22919255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphisms of DNA repair gene XRCC1 and hepatocellular carcinoma risk among East Asians: a meta-analysis.Tumour Biol. 2013 Feb;34(1):261-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0546-5. Epub 2012 Oct 6. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23055199
-
A meta-analysis of XRCC1 single nucleotide polymorphism and susceptibility to gynecological malignancies.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Dec 17;100(50):e28030. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028030. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34918657 Free PMC article.
-
XRCC1 Arg399Gln genetic polymorphism and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Feb;41(2):879-87. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2929-0. Epub 2014 Jan 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24390232
-
The XRCC1 Arg399Gln genetic polymorphism contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility: an updated meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(10):5761-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.10.5761. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24289575
Cited by
-
Molecular Bases of Drug Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 23;12(6):1663. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061663. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32585893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The critical role of circular RNAs in drug resistance in gastrointestinal cancers.Med Oncol. 2023 Mar 14;40(4):116. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-01980-4. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36917431 Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the correlation between base-excision repair gene SNPs and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk in a Chinese Han population.Mol Clin Oncol. 2020 Aug;13(2):228-236. doi: 10.3892/mco.2020.2066. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Mol Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32714550 Free PMC article.
-
Association of XRCC1 p. Arg194Trp gene polymorphism with the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV Egyptian population: A pilot case-control study.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241265263. doi: 10.1177/03946320241265263. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38898405 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Ten Core Hub Genes as Potential Biomarkers and Treatment Target for Hepatoblastoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 1;11:591507. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.591507. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33868991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seguí N, Mina LB, Lázaro C, Sanz-Pamplona R, Pons T, Navarro M, Bellido F, López-Doriga A, Valdés-Mas R, Pineda M, et al.: Germline mutations in FAN1 cause hereditary colorectal cancer by impairing DNA repair. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149(3): 563–566. Epub 2015/06/05; - PubMed
-
- Huang X, Liu C, Cui Y, Zhang H, Liu Y, Zhou X, et al. Association between XRCC1 and ERCC1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms and the efficacy of concurrent radiochemotherapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2017; 13(2):704–714. Epub 2016 Dec 14. 10.3892/ol.2016.5496 17(1):758. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

