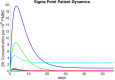
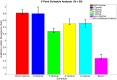
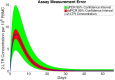
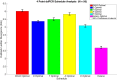
HIV 2-LTR experiment design optimization
- PMID: 30408070
- PMCID: PMC6224063
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206700
HIV 2-LTR experiment design optimization
Abstract
Clinical trials are necessary in order to develop treatments for diseases; however, they can often be costly, time consuming, and demanding to the patients. This paper summarizes several common methods used for optimal design that can be used to address these issues. In addition, we introduce a novel method for optimizing experiment designs applied to HIV 2-LTR clinical trials. Our method employs Bayesian techniques to optimize the experiment outcome by maximizing the Expected Kullback-Leibler Divergence (EKLD) between the a priori knowledge of system parameters before the experiment and the a posteriori knowledge of the system parameters after the experiment. We show that our method is robust and performs equally well if not better than traditional optimal experiment design techniques.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: RZ is named as an inventor on US Patent 9874563, “Detecting and quantifying cryptic HIV replication.” RZ provides consulting to Merck, Sharp, and Dohme, Corp. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimal Bayesian design for patient selection in a clinical study.Biometrics. 2009 Sep;65(3):953-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-0420.2008.01156.x. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Biometrics. 2009. PMID: 19021600
-
A Bayesian approach to parameter estimation in HIV dynamical models.Stat Med. 2002 Aug 15;21(15):2199-214. doi: 10.1002/sim.1211. Stat Med. 2002. PMID: 12210633
-
Exploratory Bayesian model selection for serial genetics data.Biometrics. 2005 Jun;61(2):591-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1541-0420.2005.040417.x. Biometrics. 2005. PMID: 16011709
-
Viral phenotype and genotype as markers in clinical trials.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995;10 Suppl 2:S25-34. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995. PMID: 7552510 Review.
-
A Bayesian approach for inference from a bridging study with binary outcomes.J Biopharm Stat. 2012 Sep;22(5):935-51. doi: 10.1080/10543406.2012.698436. J Biopharm Stat. 2012. PMID: 22946941 Review.
Cited by
-
Significant Unresolved Questions and Opportunities for Bioengineering in Understanding and Treating COVID-19 Disease Progression.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020 Jul 27;13(4):259-284. doi: 10.1007/s12195-020-00637-w. eCollection 2020 Aug. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020. PMID: 32837585 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing in a Direct Model of HIV Infection Reveals Important Parallels to and Differences from In Vivo Reservoir Dynamics.J Virol. 2020 Apr 16;94(9):e01900-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01900-19. Print 2020 Apr 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32051279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Emery AF, Nenarokomov AV. Optimal experiment design. Measurement Science and Technology. 1998;9: 864–876. 10.1088/0957-0233/9/6/003 - DOI
-
- Chaloner K, Verdinelli I. Bayesian experimental design: A review. Statistical Science. 1995;10: 273–304. 10.1214/ss/1177009939 - DOI
-
- Bankert EA, Amdur RJ. Institutional Review Board: Management and Function. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases