Eustachian tube dysfunction: A diagnostic accuracy study and proposed diagnostic pathway
- PMID: 30408100
- PMCID: PMC6224095
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206946
Eustachian tube dysfunction: A diagnostic accuracy study and proposed diagnostic pathway
Abstract
Background and aims: Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a commonly diagnosed disorder of Eustachian tube opening and closure, which may be associated with severe symptoms and middle ear disease. Currently the diagnosis of obstructive and patulous forms of ETD is primarily based on non-specific symptoms or examination findings, rather than measurement of the underlying function of the Eustachian tube. This has proved problematic when selecting patients for treatment, and when designing trial inclusion criteria and outcomes. This study aims to determine the correlation and diagnostic value of various tests of ET opening and patient reported outcome measures (PROMs), in order to generate a recommended diagnostic pathway for ETD.
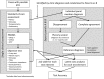
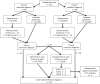
Methods: Index tests included two PROMs and 14 tests of ET opening (nine for obstructive, five for patulous ETD). In the absence of an accepted reference standard two methods were adopted to establish index test accuracy: expert panel diagnosis and latent class analysis. Index test results were assessed with Pearson correlation and principle component analysis, and test accuracy was determined. Logistic regression models assessed the predictive value of grouped test results.
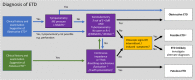
Results: The expert panel diagnosis and PROMs results correlated with each other, but not with ET function measured by tests of ET opening. All index tests were found to be feasible in clinic, and acceptable to patients. PROMs had very poor specificity, and no diagnostic value. Combining the results of tests of ET function appeared beneficial. The latent class model suggested tympanometry, sonotubometry and tubomanometry have the best diagnostic performance for obstructive ETD, and these are included in a proposed diagnostic pathway.
Conclusions: ETD should be diagnosed on the basis of clinical assessment and tests of ET opening, as PROMs have no diagnostic value. Currently diagnostic uncertainty exists for some patients who appear to have intermittent ETD clinically, but have negative index test results.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

