Caprine herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) as a potential candidate for oncolytic virotherapy
- PMID: 30409104
- PMCID: PMC6343687
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1504722
Caprine herpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) as a potential candidate for oncolytic virotherapy
Abstract
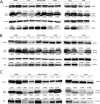
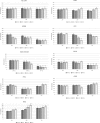
Caprine Herpesvirus type 1 (CpHV-1) is a species-specific herpes virus able to induce apoptosis in several biological systems. In the present study we aimed to investigate the ability of CpHV-1 to reduce cells viability, to replicate and to cause cell death also in human cancer cell lines. We tested the CpHV-1 effects on HEL-299, Vero, MDA-MB-468, HeLa, U2OS, PC3, A549 and K562 neoplastic cell lines and on MDBK cells. Firstly, we evaluated the effect of CpHV-1 infection on cell viability by MTT assay and our data showed that CpHV-1 can induce a marked cytopathic effect (CPE) in most of cell lines tested, except for HEL-299, Vero and K562 cells. The reduction of cell viability was associated with a significant increase of viral production. We next investigated if CpHV-1 was able to induce cell death and so through western blotting analysis we evaluated cleaved caspase 3, LC3II and p62 protein levels after infection. Caspase 3 activation was detected in MDBK cells and, even if at different times p.i., also in MDA-MB-468, U2OS, and PC3 cell lines, while LC3II increase and concomitant p62 protein reduction were observed only in U2OS, and A549 cells, no significant alteration of these proteins was observed in the other cell lines tested. Finally, to confirm virus ability to trigger apoptosis we performed an Annexin-V apoptosis test after 24 h p.i. Although we need to further explore mechanisms underlying CpHV-1 treatment, this study could serve as the basis for the development of new treatment options aiming to fight several cancer types.
Keywords: Oncolytic virotherapy; apoptosis; autophagy; human cancer cells.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
