Propofol vs. inhalational agents to maintain general anaesthesia in ambulatory and in-patient surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30409186
- PMCID: PMC6225663
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-018-0632-3
Propofol vs. inhalational agents to maintain general anaesthesia in ambulatory and in-patient surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: It is unclear if anaesthesia maintenance with propofol is advantageous or beneficial over inhalational agents. This study is intended to compare the effects of propofol vs. inhalational agents in maintaining general anaesthesia on patient-relevant outcomes and patient satisfaction.
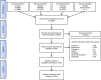
Methods: Studies were identified by electronic database searches in PubMed™, EMBASE™ and the Cochrane™ library between 01/01/1985 and 01/08/2016. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of peer-reviewed journals were studied. Of 6688 studies identified, 229 RCTs were included with a total of 20,991 patients. Quality control, assessment of risk of bias, meta-bias, meta-regression and certainty in evidence were performed according to Cochrane. Common estimates were derived from fixed or random-effects models depending on the presence of heterogeneity. Post-operative nausea and vomiting (PONV) was the primary outcome. Post-operative pain, emergence agitation, time to recovery, hospital length of stay, post-anaesthetic shivering and haemodynamic instability were considered key secondary outcomes.
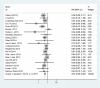
Results: The risk for PONV was lower with propofol than with inhalational agents (relative risk (RR) 0.61 [0.53, 0.69], p < 0.00001). Additionally, pain score after extubation and time in the post-operative anaesthesia care unit (PACU) were reduced with propofol (mean difference (MD) - 0.51 [- 0.81, - 0.20], p = 0.001; MD - 2.91 min [- 5.47, - 0.35], p = 0.03). In turn, time to respiratory recovery and tracheal extubation were longer with propofol than with inhalational agents (MD 0.82 min [0.20, 1.45], p = 0.01; MD 0.70 min [0.03, 1.38], p = 0.04, respectively). Notably, patient satisfaction, as reported by the number of satisfied patients and scores, was higher with propofol (RR 1.06 [1.01, 1.10], p = 0.02; MD 0.13 [0.00, 0.26], p = 0.05). Secondary analyses supported the primary results.
Conclusions: Based on the present meta-analysis there are several advantages of anaesthesia maintenance with propofol over inhalational agents. While these benefits result in an increased patient satisfaction, the clinical and economic relevance of these findings still need to be addressed in adequately powered prospective clinical trials.
Keywords: Desflurane; Inhalational Anaesthesia; Isoflurane; Patient Reported Outcomes; Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting; Postoperative Pain; Propofol; Sevoflurane; Target Controlled Infusion; Total Intravenous Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The manuscript is a systematic review and meta-analysis and as such data study reporting on published material. Therefore, no Ethics approval is required. The project was registered at PROSPERO, 22 July 2016, registration number CRD42016039539.
Consent for publication
As this is no clinical study but a report on data analysis on published material, consent to publish consent does not apply.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Jellish WS, Lien CA, Fontenot HJ, Hall R. The comparative effects of sevoflurane versus propofol in the induction and maintenance of anesthesia in adult patients. Anesth Analg. 1996;82:479–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

