An update on sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 modulators
- PMID: 30409535
- PMCID: PMC6430570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.10.042
An update on sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 modulators
Abstract
Sphingolipids represent an essential class of lipids found in all eukaryotes, and strongly influence cellular signal transduction. Autoimmune diseases like asthma and multiple sclerosis (MS) are mediated by the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) to express a variety of symptoms and disease patterns. Inspired by its natural substrate, an array of artificial sphingolipid derivatives has been developed to target this specific G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) in an attempt to suppress autoimmune disorders. FTY720, also known as fingolimod, is the first oral disease-modifying therapy for MS on the market. In pursuit of improved stability, bioavailability, and efficiency, structural analogues of this initial prodrug have emerged over time. This review covers a brief introduction to the sphingolipid metabolism, the mechanism of action on S1P1, and an updated overview of synthetic sphingosine S1P1 agonists.
Keywords: Autoimmune modulators; S1P(1) agonists; Sphingolipids; Sphingosine-1-phosphate; Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
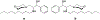
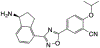

References
-
- Spiegel S; English D; Milstien S Trends in Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 236–242. - PubMed
-
- Thudichum JLW A Treatise on the Chemical Constitution of the Brain, Bailliere and Cox, 1884.
-
- Klenk E; Diebold W Z. Physiol. Chem 1931, 198, 25–32.
-
- Carter HE; Glick FJ; Norris WP; Phillips GE J. Biol. Chem 1942, 142, 449–450.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical

