Risk Factor Modeling for Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes in the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications (EDC) Study: A Comparison With the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Study (DCCT/EDIC)
- PMID: 30409781
- PMCID: PMC6341302
- DOI: 10.2337/db18-0515
Risk Factor Modeling for Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes in the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications (EDC) Study: A Comparison With the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Study (DCCT/EDIC)
Abstract
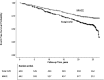
In a recent Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT)/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study report, mean HbA1c was the strongest predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD) after age. In DCCT/EDIC, mean diabetes duration was 6 years (median 4) at baseline and those with high blood pressure or cholesterol were excluded. We now replicate these analyses in the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications (EDC) prospective cohort study of childhood-onset (at <17 years of age) type 1 diabetes, with similar age (mean 27 years in both studies) but longer diabetes duration (mean 19 years and median 18 years) and no CVD risk factor exclusion at baseline. CVD incidence (CVD death, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, revascularization, angina, or ischemic electrocardiogram) was associated with diabetes duration, most recent albumin excretion rate (AER), updated mean triglycerides, baseline hypertension, baseline LDL cholesterol, and most recent HbA1c Major atherosclerotic cardiovascular events (CVD death, MI, or stroke) were associated with diabetes duration, most recent AER, baseline systolic blood pressure, baseline smoking, and updated mean HbA1c Compared with findings in DCCT/EDIC, traditional risk factors similarly predicted CVD; however AER predominates in EDC and HbA1c in DCCT/EDIC. Thus, the relative impact of HbA1c and kidney disease in type 1 diabetes varies according to diabetes duration.
© 2018 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Huxley RR, Peters SA, Mishra GD, Woodward M. Risk of all-cause mortality and vascular events in women versus men with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2015;3:198–206 - PubMed
-
- Orchard TJ, Costacou T. Cardiovascular complications of type 1 diabetes: update on the renal link. Acta Diabetol 2017;54:325–334 - PubMed
-
- Orchard TJ. Dyslipoproteinemia and diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1990;19:361–380 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous