Influence of Stereochemistry on the Bioactivation and Glucuronidation of 4-Ipomeanol
- PMID: 30409834
- PMCID: PMC6346377
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.118.249771
Influence of Stereochemistry on the Bioactivation and Glucuronidation of 4-Ipomeanol
Abstract
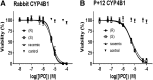
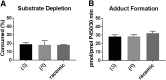
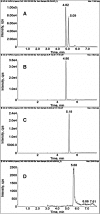
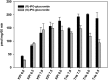
A potential CYP4B1 suicide gene application in engineered T-cell treatment of blood cancers has revived interest in the use of 4-ipomeanol (IPO) in gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy, in which disposition of the administered compound may be critical. IPO contains one chiral center at the carbon bearing a secondary alcohol group; it was of interest to determine the effect of stereochemistry on 1) CYP4B1-mediated bioactivation and 2) (UGT)-mediated glucuronidation. First, (R)-IPO and (S)-IPO were synthesized and used to assess cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells expressing rabbit CYP4B1 and re-engineered human CYP4B1, where the enantiomers were found to be equipotent. Next, a sensitive UPLC-MS/MS assay was developed to measure the IPO-glucuronide diastereomers and product stereoselectivity in human tissue microsomes. Human liver and kidney microsomes generated (R)- and (S)-IPO-glucuronide diastereomers in ratios of 57:43 and 79:21, respectively. In a panel of 13 recombinantly expressed UGTs, UGT1A9 and UGT2B7 were the major isoforms responsible for IPO glucuronidation. (R)-IPO-glucuronide diastereoselectivity was apparent with each recombinant UGT, except UGT2B15 and UGT2B17, which favored the formation of (S)-IPO-glucuronide. Incubations with IPO and the UGT1A9-specific chemical inhibitor niflumic acid significantly decreased glucuronidation in human kidney, but only marginally in human liver microsomes, consistent with known tissue expression patterns of UGTs. We conclude that IPO glucuronidation in human kidney is mediated by UGT1A9 and UGT2B7. In human liver, it is mediated primarily by UGT2B7 and, to a lesser extent, UGT1A9 and UGT2B15. Overall, the lack of pronounced stereoselectivity for IPO's bioactivation in CYP4B1-transfected HepG2 cells, or for hepatic glucuronidation, suggests the racemate is an appropriate choice for use in suicide gene therapies.
Copyright © 2019 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Species Differences in Microsomal Oxidation and Glucuronidation of 4-Ipomeanol: Relationship to Target Organ Toxicity.Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 Oct;44(10):1598-602. doi: 10.1124/dmd.116.070003. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016. PMID: 27468999 Free PMC article.
-
Glucuronidation of edaravone by human liver and kidney microsomes: biphasic kinetics and identification of UGT1A9 as the major UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoform.Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Apr;40(4):734-41. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.043356. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012. PMID: 22238289
-
Generation and characterization of a Cyp4b1 null mouse and the role of CYP4B1 in the activation and toxicity of Ipomeanol.Toxicol Sci. 2013 Aug;134(2):243-50. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft123. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Toxicol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23748241 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases involved in N-carbamoyl glucuronidation of lorcaserin.Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Apr;40(4):772-8. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.043448. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012. PMID: 22259019
-
Stereoselective conjugation of oxazepam by human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs): S-oxazepam is glucuronidated by UGT2B15, while R-oxazepam is glucuronidated by UGT2B7 and UGT1A9.Drug Metab Dispos. 2002 Nov;30(11):1257-65. doi: 10.1124/dmd.30.11.1257. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002. PMID: 12386133
Cited by
-
Human Family 1-4 cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the metabolic activation of xenobiotic and physiological chemicals: an update.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Feb;95(2):395-472. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02971-4. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33459808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez-Diez TM, Zheng J. (2004) Mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome P450 3A4 by 4-ipomeanol. Chem Res Toxicol 17:150–157. - PubMed
-
- Baer BR, Rettie AE, Henne KR. (2005) Bioactivation of 4-ipomeanol by CYP4B1: adduct characterization and evidence for an enedial intermediate. Chem Res Toxicol 18:855–864. - PubMed
-
- Baldelli S, Merlini S, Perico N, Nicastri A, Cortinovis M, Gotti E, Remuzzi G, Cattaneo D. (2007) C-440T/T-331C polymorphisms in the UGT1A9 gene affect the pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid in kidney transplantation. Pharmacogenomics 8:1127–1141. - PubMed
-
- Boyd MR, Wilson BJ, Harris TM. (1972) Confirmation by chemical synthesis of the structure of 4-ipomeanol, a lung-toxic metabolite of the sweet potato, Ipomoea batatas. Nat New Biol 236:158–159. - PubMed
-
- Court MH. (2005) Isoform-selective probe substrates for in vitro studies of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Methods Enzymol 400:104–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

