Chiral lipidomics of monoepoxy and monohydroxy metabolites derived from long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids
- PMID: 30409844
- PMCID: PMC6314268
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M089755
Chiral lipidomics of monoepoxy and monohydroxy metabolites derived from long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids
Abstract
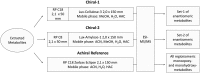
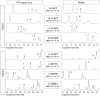
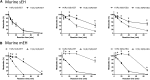
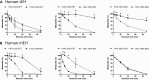
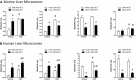
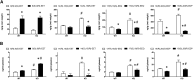
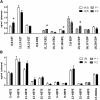
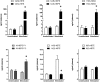
A chiral lipidomics approach was established for comprehensive profiling of regio- and stereoisomeric monoepoxy and monohydroxy metabolites of long-chain PUFAs as generated enzymatically by cytochromes P450 (CYPs), lipoxygenases (LOXs), and cyclooxygenases (COXs) and, in part, also unspecific oxidations. The method relies on reversed-phase chiral-LC coupled with ESI/MS/MS. Applications revealed partially opposing enantioselectivities of soluble and microsomal epoxide hydrolases (mEHs). Ablation of the soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) gene resulted in specific alterations in the enantiomeric composition of endogenous monoepoxy metabolites. For example, the (R,S)/(S,R)-ratio of circulating 14,15-EET changed from 2.1:1 in WT to 9.7:1 in the sEH-KO mice. Studies with liver microsomes suggested that CYP/mEH interactions play a primary role in determining the enantiomeric composition of monoepoxy metabolites during their generation and release from the ER. Analysis of human plasma showed significant enantiomeric excess with several monoepoxy metabolites. Monohydroxy metabolites were generally present as racemates; however, Ca2+-ionophore stimulation of whole blood samples resulted in enantioselective increases of LOX-derived metabolites (12S-HETE and 17S-hydroxydocosahexaenoic acid) and COX-derived metabolites (11R-HETE). Our chiral approach may provide novel opportunities for investigating the role of bioactive lipid mediators that generally exert their physiological functions in a highly regio- and stereospecific manner.
Keywords: chiral high-performance liquid chromatography; cytochrome P450; eicosanoids; lipoxygenase; microsomal epoxide hydrolase; oxylipins; soluble epoxide hydrolase; stereoisomers; tandem mass spectrometry.
Copyright © 2019 Blum et al.
Figures

References
-
- Willenberg I., Ostermann A. I., and Schebb N. H.. 2015. Targeted metabolomics of the arachidonic acid cascade: current state and challenges of LC-MS analysis of oxylipins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 407: 2675–2683. - PubMed
-
- Schunck W. H., Konkel A., Fischer R., and Weylandt K. H.. 2018. Therapeutic potential of omega-3 fatty acid-derived epoxyeicosanoids in cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 183: 177–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

