Silencing of Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group D Gene Promotes Hepatoma Cell Growth by Reducing P53 Expression
- PMID: 30409962
- PMCID: PMC6238547
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.910944
Silencing of Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group D Gene Promotes Hepatoma Cell Growth by Reducing P53 Expression
Abstract
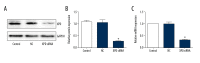
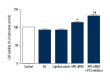
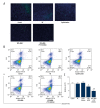
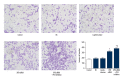
BACKGROUND This study investigated the effect of xeroderma pigmentosum group D (XPD) silencing on the growth of hepatoma cells and assessed the mechanisms. MATERIAL AND METHODS XPD gene was silenced by siRNA in hepatoma cells. The experiments were randomly divided into a control group, a liposome control group, a negative control (NC) group, an XPD siRNA group, and an XPD siRNA + P53 inhibitor group. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) was used to detect cell viability 24 h after gene silencing and treatments. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferases (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) and flow cytometry were used to detect apoptosis. Invasive ability was detected by Transwell assay. Additionally, the expression of mouse double-minute 2 homolog (Mdm2), mouse double-minute 4 homolog (Mdm4), CyclinD1, P21, Bax, P53, C-sis, and Bcl-2 was detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting. RESULTS Compared with the NC group, XPD siRNA significantly reduced XPD expression at both mRNA and protein levels. XPD siRNA significantly promoted cell proliferation, reduced apoptosis, and promoted cell invasive ability. Expression of CyclinD1, Bcl-2, and C-sis increased significantly after XPD silencing, while the expression of P21, Mdm2, Mdm4, Bax, and P53 significantly decreased (vs. NC, P<0.05). Importantly, P53 inhibitor (1 μM bpV) further enhanced the effect of XPD silencing (vs. XPD silencing, P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS Our data revealed that XPD silencing promoted growth of hepatoma cells by reducing P53 expression.
Figures
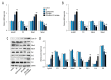
References
-
- Fang Y, He J, Janssen HLA, et al. Peroxiredoxin 1, restraining cell migration and invasion, is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. J Dig Dis. 2018;19:155–69. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

