Elevated serum IL-6 and adiponectin levels are associated with frailty and physical function in Chinese older adults
- PMID: 30410318
- PMCID: PMC6197209
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S180934
Elevated serum IL-6 and adiponectin levels are associated with frailty and physical function in Chinese older adults
Abstract
Purpose: Frailty is associated with adverse health outcomes. Its biological markers are essential to enhance diagnostic ease and would contribute to surveillance of the condition. Considering the involvement of pro-inflammatory and nutritional states in frailty, we aimed to investigate whether inflammatory mediators and adipokines are associated with frailty and their relationship with physical function.
Patients and methods: We recruited 130 older adults (90 nonfrail participants and 40 frail participants, mean age: 72.80±8.61 years) who underwent a comprehensive medical history and frailty assessment. The biochemical indicators (eg, blood urea nitrogen [BUN], high-density lipoprotein [HDL], and hemoglobin [HGB]), insulin pathway (glucose, insulin, and insulin-like growth factor 1 [IGF-1]), circulating inflammatory biomarkers (IL-6, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1, and C-reactive protein), and adipokines (adiponectin, vaspin, and leptin) were compared between the two groups. We further analyzed their correlation with physical function.
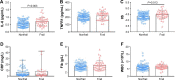
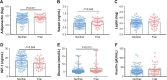
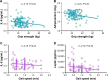
Results: Frail older adults showed higher levels of BUN, IL-6, adiponectin, vaspin, and glucose and lower levels of IGF-1, HDL, and HGB compared with nonfrail participants. Serum IL-6 levels were negatively correlated with both grip strength (P=0.03) and gait speed (P=0.04). Levels of circulating adiponectin and leptin were adversely correlated with grip strength (P=0.01) and gait speed (P=0.03), respectively. After adjustment for age and sex, the only markers correlated with physical function were IL-6 (r=-0.180, P=0.044) and adiponectin (r=-0.195, P=0.029).
Conclusion: High levels of IL-6, adiponectin, vaspin, and glucose as well as low levels of IGF-1 were found in frail older adults. Furthermore, IL-6, adiponectin, and leptin levels were negatively correlated with physical function, suggesting that inflammatory mediators and adipokines are biomarkers for frailty and decreased function in older adults.
Keywords: IL-6; adipokine; adiponectin; biomarker; frailty; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum SIRT1 Is Associated with Frailty and Adipokines in Older Adults.J Nutr Health Aging. 2019;23(3):246-250. doi: 10.1007/s12603-018-1149-7. J Nutr Health Aging. 2019. PMID: 30820512 Free PMC article.
-
Frailty status and altered dynamics of circulating energy metabolism hormones after oral glucose in older women.J Nutr Health Aging. 2012 Aug;16(8):679-86. doi: 10.1007/s12603-012-0066-4. J Nutr Health Aging. 2012. PMID: 23076509
-
The acute inflammatory response after trauma is heightened by frailty: A prospective evaluation of inflammatory and endocrine system alterations in frailty.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019 Jul;87(1):54-60. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000002229. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2019. PMID: 30768559
-
Association between obesity-related adipokines and colorectal cancer: a case-control study and meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 28;20(24):7941-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7941. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24976730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-based biomarkers of frailty in older patients with cancer.Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2025 Mar 1;19(1):25-32. doi: 10.1097/SPC.0000000000000747. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2025. PMID: 39888831 Review.
Cited by
-
[Characteristics of geriatric and somatic status in patients with osteoporosis].Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 2021 Jun 17;67(3):45-54. doi: 10.14341/probl12751. Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 2021. PMID: 34297501 Free PMC article. Russian.
-
Inflammatory biomarkers in older adults with frailty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022 May;34(5):971-987. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-02022-7. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022. PMID: 34981430
-
Bidirectional Longitudinal Study of Frailty and Depressive Symptoms Among Older Chinese Adults.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Feb 10;14:791971. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.791971. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35221990 Free PMC article.
-
CT-measured skeletal muscle mass used to assess frailty in patients with head and neck cancer.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019 Oct;10(5):1060-1069. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12443. Epub 2019 May 27. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019. PMID: 31134765 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional causal associations between frailty measures and sleep disturbances: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Nat Sci Sleep. 2025 Feb 7;17:271-284. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S497173. eCollection 2025. Nat Sci Sleep. 2025. PMID: 39936043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56(3):M146–M157. - PubMed
-
- Nagasawa M, Takami Y, Akasaka H, et al. High plasma adiponectin levels are associated with frailty in a general old-old population: The Septuagenarians, Octogenarians, Nonagenarians Investigation with Centenarians study. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018;18(6):839–846. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

