Targeting VEGF pathway to normalize the vasculature: an emerging insight in cancer therapy
- PMID: 30410348
- PMCID: PMC6200071
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S172042
Targeting VEGF pathway to normalize the vasculature: an emerging insight in cancer therapy
Abstract
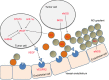
Vascular normalization is a new concept of targeting angiogenesis to restore vessel structure and function and to increase blood perfusion and delivery of drugs. It has been confirmed that vascular normalization can decrease relapse and benefit other cancer therapy, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immune cell therapy. The key point of this therapy is to inhibit pro-angiogenic factors and make it be balanced with anti-angiogenic factors, resulting in a mature and normal vessel characteristic. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a key player in the process of tumor angiogenesis, and inhibiting VEGF is a primary approach to tumor vessel normalization. Herein, we review newly uncovered mechanisms governing angiogenesis and vascular normalization of cancer and place emphasis on targeting VEGF pathway to normalize the vasculature. Also, important methods to depress VEGF pathway and make tumor vascular are discussed.
Keywords: anti-angiogenesis; cancer therapy; treatment resistance; vascular endothelial growth factor; vascular normalization.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Gerlowski LE, Jain RK. Microvascular permeability of normal and neoplastic tissues. Microvasc Res. 1986;31(3):288–305. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Transport of molecules across tumor vasculature. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1987;6(4):559–593. - PubMed
-
- Stohrer M, Boucher Y, Stangassinger M, Jain RK. Oncotic pressure in solid tumors is elevated. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4251–4255. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Determinants of tumor blood flow: a review. Cancer Res. 1988;48(10):2641–2658. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

