The role of inhaled methoxyflurane in acute pain management
- PMID: 30410414
- PMCID: PMC6200081
- DOI: 10.2147/OAEM.S181222
The role of inhaled methoxyflurane in acute pain management
Abstract
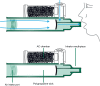
Methoxyflurane is an inhaled analgesic administered via a disposable inhaler which has been used in Australia for over 40 years for the management of pain associated with trauma and for medical procedures in children and adults. Now available in 16 countries worldwide, it is licensed in Europe for moderate to severe pain associated with trauma in conscious adults, although additional applications are being made to widen the range of approved indications. Considering these ongoing developments, we reviewed the available evidence on clinical usage and safety of inhaled analgesic methoxyflurane in trauma pain and in medical procedures in both adults and children. Published data on methoxyflurane in trauma and procedural pain show it to be effective, well tolerated, and highly rated by patients, providing rapid onset of analgesia. Methoxyflurane has a well-established safety profile; adverse events are usually brief and self-limiting, and no clinically significant effects on vital signs or consciousness levels have been reported. Nephrotoxicity previously associated with methoxyflurane at high anesthetic doses is not reported with low analgesic doses. Although two large retrospective comparative studies in the prehospital setting showed inhaled analgesic methoxyflurane to be less effective than intravenous morphine and intranasal fentanyl, this should be balanced against the administration, supervision times, and safety profile of these agents. Given the limitations of currently available analgesic agents in the prehospital and emergency department settings, the ease of use and portability of methoxyflurane combined with its rapid onset of effective pain relief and favorable safety profile make it a useful nonopioid option for pain management. Except for the STOP! study, which formed the basis for approval in trauma pain in Europe, and a few smaller randomized controlled trials (RCTs), much of the available data are observational or retrospective, and further RCTs are currently underway to provide more robust data.
Keywords: Penthrox; analgesia; clinical safety; procedural pain; review; trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure KMP, ADD, and PMM have previously served as speakers, consultants, and advisory board members for Mundipharma International Limited and Medical Developments International. SD is an employee of Mundipharma International Limited. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Tomlin PJ. Methoxyflurane. Br J Anaesth. 1965;37(9):706–709. - PubMed
-
- Stephen CR. Clinical applications of methoxyflurane. Acta Anaesthe-siol Scand Suppl. 1966;24:215–222. - PubMed
-
- Mazze RI. Methoxyflurane revisited: tale of an anesthetic from cradle to grave. Anesthesiology. 2006;105(4):843–846. - PubMed
-
- Tomi K, Mashimo T, Tashiro C, et al. Alterations in pain threshold and psychomotor response associated with subanaesthetic concentrations of inhalation anaesthetics in humans. Br J Anaesth. 1993;70(6):684–686. - PubMed
-
- Crandell WB, Pappas SG, Macdonald A. Nephrotoxicity associated with methoxyflurane anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1966;27(5):591–607. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases