The first year of the global Enhanced Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Programme (EGASP) in Bangkok, Thailand, 2015-2016
- PMID: 30412586
- PMCID: PMC6226150
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206419
The first year of the global Enhanced Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Programme (EGASP) in Bangkok, Thailand, 2015-2016
Abstract
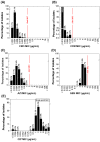
Antimicrobial-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG) infection is a global public health threat, and there is a critical need to monitor patterns of resistance and risk factors. In collaboration with the World Health Organization (WHO), the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the Thailand Department of Disease Control (DDC), Ministry of Public Health (MoPH) implemented the first Enhanced Gonococcal Antimicrobial Surveillance Programme (EGASP) in November 2015. Men presenting with urethritis at two clinical settings in Bangkok, Thailand (Bangrak Hospital [BH] and Silom Community Clinic @TropMed [SCC @TropMed]) provided demographic and behavioral information and had a urethral swab for Gram's stain and NG culture collected. The NG isolates were evaluated for antimicrobial susceptibility by the Epsilometer test (Etest) to determine minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for cefixime (CFM), ceftriaxone (CRO), azithromycin (AZI), gentamicin (GEN), and ciprofloxacin (CIP). From November 2015 -October 2016, 1,102 specimens were collected from 1,026 symptomatic men; 861 (78.1%) specimens were from BH and 241 (21.9%) specimens were from SCC @TropMed. Among the 1,102 specimens, 582 (52.8%) had intracellular Gram-negative diplococci and 591 (53.6%) had NG growth (i.e., NG infection); antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) was performed on 590 (99.8%) NG isolates. Among all symptomatic men, 293 (28.6%) had sex with men only, 430 (41.9%) were ages 18-29 years, 349 (34.0%) had antibiotic use in the last 2 weeks, and 564 (55.0%) had NG infection. Among 23 men with repeat NG infection during this first year of surveillance, 20 (87.0%) were infected twice, 2 (8.7%) were infected three times, and 1 (4.3%) was infected more than four times. All NG isolates were susceptible to CFM and CRO, and had MICs below 2 μg/mL for AZI and below 16 μg/mL for GEN. Overall, 545 (92.4%) isolates were resistant to CIP. This surveillance activity assessed individual patients, and included demographic and behavioral data linked to laboratory data. The inclusion of both individual and laboratory information in EGASP could help identify possible persistent infection and NG treatment failures. Expansion of EGASP to additional global settings is critical to assess trends and risk factors for NG, and to monitor for the emergence of resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Guidelines for the Treatment of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. Geneva2016.
-
- Bureau of AIDS, TB and STIs, Department of Disease Control, Ministry of Public Health of Thailand. Guidelines for the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases 2015. 1 ed Bangkok: Bangrak STIs Cluster; 2015.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update to CDC's Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2010: oral cephalosporins no longer a recommended treatment for gonococcal infections. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012;61(31):590–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

