Neonatal Lung Disease Associated with TBX4 Mutations
- PMID: 30413314
- PMCID: PMC6389379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.10.018
Neonatal Lung Disease Associated with TBX4 Mutations
Abstract
Variable lung disease was documented in 2 infants with heterozygous TBX4 mutations; their clinical presentations, pathology, and outcomes were distinct. These findings demonstrate that TBX4 gene mutations are associated with neonatal respiratory failure and highlight the wide spectrum of clinicopathological outcomes that have implications for patient diagnosis and management.
Keywords: ABCA3; T-box transcription factor; TBX2; TBX4; congenital alveolar dysplasia; congenital anomaly; lung development; pulmonary hypoplasia.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
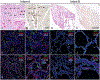

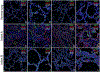
References
-
- Chow CW, Massie J, Ng J, Mills J, Baker M. Acinar dysplasia of the lungs: variation in the extent of involvement and clinical features. Pathology. 2013;45:38–43. - PubMed
-
- Langston C, Dishop MK. Diffuse lung disease in infancy: a proposed classification applied to 259 diagnostic biopsies. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2009;12:421–37. - PubMed
-
- Barnett CP, Nataren NJ, Klingler-Hoffmann M, Schwarz Q, Chong CE, Lee YK, et al. Ectrodactyly and Lethal Pulmonary Acinar Dysplasia Associated with Homozygous FGFR2 Mutations Identified by Exome Sequencing. Human mutation. 2016;37:955–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

