Cryptic binding sites become accessible through surface reconstruction of the type I collagen fibril
- PMID: 30413772
- PMCID: PMC6226522
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34616-z
Cryptic binding sites become accessible through surface reconstruction of the type I collagen fibril
Abstract
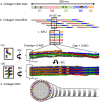
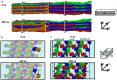
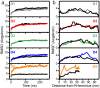
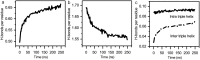
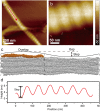
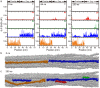
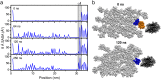
Collagen fibril interactions with cells and macromolecules in the extracellular matrix drive numerous cellular functions. Binding motifs for dozens of collagen-binding proteins have been determined on fully exposed collagen triple helical monomers. However, when the monomers are assembled into the functional collagen fibril, many binding motifs become inaccessible, and yet critical cellular processes occur. Here, we have developed an early stage atomic model of the smallest repeating unit of the type I collagen fibril at the fibril surface that provides a novel framework to address questions about these functionally necessary yet seemingly obstructed interactions. We use an integrative approach by combining molecular dynamics (MD) simulations with atomic force microscopy (AFM) experiments and show that reconstruction of the collagen monomers within the complex fibril play a critical role in collagen interactions. In particular, the fibril surface shows three major conformational changes, which allow cryptic binding sites, including an integrin motif involved in platelet aggregation, to be exposed. The observed dynamics and reconstruction of the fibril surface promote its role as a "smart fibril" to keep certain binding sites cryptic, and to allow accessibility of recognition domains when appropriate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Vogel WF. Collagen-receptor signaling in health and disease. Eur J Dermatol. 2001;11:506–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

