Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum as a Paradigm of Heritable Ectopic Mineralization Disorders: Pathomechanisms and Treatment Development
- PMID: 30414410
- PMCID: PMC6412714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.09.014
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum as a Paradigm of Heritable Ectopic Mineralization Disorders: Pathomechanisms and Treatment Development
Abstract
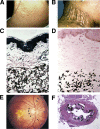
Ectopic mineralization is a global problem and leading cause of morbidity and mortality. The pathomechanisms of ectopic mineralization are poorly understood. Recent studies on heritable ectopic mineralization disorders with defined gene defects have been helpful in elucidation of the mechanisms of ectopic mineralization in general. The prototype of such disorders is pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), a late-onset, slowly progressing disorder with multisystem clinical manifestations. Other conditions include generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI), characterized by severe, early-onset mineralization of the cardiovascular system, often with early postnatal demise. In addition, arterial calcification due to CD73 deficiency (ACDC) occurs late in life, mostly affecting arteries in the lower extremities in elderly individuals. These three conditions, PXE, GACI, and ACDC, caused by mutations in ABCC6, ENPP1, and NT5E, respectively, are characterized by reduced levels of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) in plasma. Because PPi is a powerful antimineralization factor, it has been postulated that reduced PPi is a major determinant for ectopic mineralization in these conditions. These and related observations on complementary mechanisms of ectopic mineralization have resulted in development of potential treatment modalities for PXE, including administration of bisphosphonates, stable PPi analogs with antimineralization activity. It is conceivable that efficient treatments may soon become available for heritable ectopic mineralization disorders with application to common calcification disorders.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Budoff M.J., Shaw L.J., Liu S.T., Weinstein S.R., Mosler T.P., Tseng P.H., Flores F.R., Callister T.Q., Raggi P., Berman D.S. Long-term prognosis associated with coronary calcification: observations from a registry of 25,253 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:1860–1870. - PubMed
-
- Neldner K.H. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Clin Dermatol. 1988;6:1–159. - PubMed
-
- Christiano A.M., Lebwohl M.G., Boyd C.D., Uitto J. Workshop on pseudoxanthoma elasticum: molecular biology and pathology of the elastic fibers: Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, June 10, 1992. J Invest Dermatol. 1992;99:660–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

