Immunoproteasome Inhibition Impairs T and B Cell Activation by Restraining ERK Signaling and Proteostasis
- PMID: 30416500
- PMCID: PMC6212513
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02386
Immunoproteasome Inhibition Impairs T and B Cell Activation by Restraining ERK Signaling and Proteostasis
Abstract
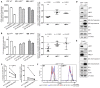
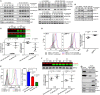
Immunoproteasome (IP) inhibition holds potential as a novel treatment option for various immune-mediated pathologies. The IP inhibitor ONX 0914 reduced T cell cytokine secretion and Th17 polarization and showed pre-clinical efficacy in a range of autoimmune disorders, transplant-allograft rejection, virus-mediated tissue damage, and colon cancer progression. However, the molecular basis of these effects has remained largely elusive. Here, we have analyzed the effects of ONX 0914 in primary human and mouse lymphocytes. ONX 0914-treatment impaired primary T cell activation in vitro and in vivo. IP inhibition reduced ERK-phosphorylation sustainment, while leaving NF-κB and other signaling pathways unaffected. Naïve T and B cells expressed nearly exclusively immuno- or mixed proteasomes but no standard proteasomes and IP inhibition but not IP-deficiency induced mild proteostasis stress, reduced DUSP5 expression and enhanced DUSP6 protein levels due to impaired degradation. However, accumulation of DUSP6 did not cause the reduced ERK-phosphorylation in a non-redundant manner. We show that broad-spectrum proteasome inhibition and immunoproteasome inhibition have distinct effects on T cell activation at the molecular level. Notably, ONX 0914-treated T cells recovered from proteostasis stress without apoptosis induction, apparently via Nrf1-mediated up-regulation of standard proteasomes. In contrast, B cells were more susceptible to apoptosis after ONX 0914-treatment. Our data thus provide mechanistic insights how IP inhibition functionally impedes T and B cells likely accounting for its therapeutic benefits.
Keywords: B cell activation; DUSP6; ERK; Nrf1; ONX 0914; T cell activation; immunoproteasome; proteostasis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ONX 0914 Lacks Selectivity for the Cardiac Immunoproteasome in CoxsackievirusB3 Myocarditis of NMRI Mice and Promotes Virus-Mediated Tissue Damage.Cells. 2020 Apr 28;9(5):1093. doi: 10.3390/cells9051093. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32354159 Free PMC article.
-
DUSP5 and DUSP6, two ERK specific phosphatases, are markers of a higher MAPK signaling activation in BRAF mutated thyroid cancers.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 14;12(9):e0184861. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184861. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28910386 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the immunoproteasome ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.EMBO Mol Med. 2014 Feb;6(2):226-38. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201303543. Epub 2014 Jan 16. EMBO Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24399752 Free PMC article.
-
A patent review of immunoproteasome inhibitors.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Jul;28(7):517-540. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2018.1484904. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018. PMID: 29865878 Review.
-
On the Role of the Immunoproteasome in Protein Homeostasis.Cells. 2021 Nov 18;10(11):3216. doi: 10.3390/cells10113216. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Catching the Big Fish in Big Data: A Meta-Analysis of Zebrafish Kidney scRNA-Seq Datasets Highlights Conserved Molecular Profiles of Macrophages and Neutrophils in Vertebrates.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;13(10):773. doi: 10.3390/biology13100773. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452082 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Proteasomes in the Thymus.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 19;12:646209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.646209. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33815406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDGF-D-induced immunoproteasome activation and cell-cell interactions.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Mar 28;21:2405-2418. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.047. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37066124 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Proteasomes in Inflammation.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 20;10(8):1783. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081783. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33923887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent insights how combined inhibition of immuno/proteasome subunits enables therapeutic efficacy.Genes Immun. 2020 Nov;21(5):273-287. doi: 10.1038/s41435-020-00109-1. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Genes Immun. 2020. PMID: 32839530 Review.
References
-
- Kuckelkorn U, Frentzel S, Kraft R, Kostka S, Groettrup M, Kloetzel PM. Incorporation of major histocompatibility complex–encoded subunits LMP2 and LMP7 changes the quality of the 20S proteasome polypeptide processing products independent of interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. (1995) 25:2605–11. 10.1002/eji.1830250930 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frentzel S, Kuhn-Hartmann I, Gernold M, Gött P, Seelig A, Kloetzel PM. The major-histocompatibility-complex-encoded beta-type proteasome subunits LMP2 and LMP7. Evidence that LMP2 and LMP7 are synthesized as proproteins and that cellular levels of both mRNA and LMP-containing 20S proteasomes are differentially regulated. Eur J Biochem. (1993) 216:119–26. 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18123.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

