Analyses of risk factors and prognosis for new-onset atrial fibrillation in elderly patients after dual-chamber pacemaker implantation
- PMID: 30416511
- PMCID: PMC6221846
- DOI: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2018.10.008
Analyses of risk factors and prognosis for new-onset atrial fibrillation in elderly patients after dual-chamber pacemaker implantation
Abstract
Objective: To retrospectively identify risk factors and the prognosis for new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) after implantation of dual-chamber pacemakers in elderly patients.
Methods: Consecutive patients aged ≥ 65 years who underwent their first implantation of a dual-chamber permanent pacemaker in Beijing Anzhen Hospital from October 2013 to May 2016 were enrolled. Their complete programming and follow-up data were recorded. Follow-up end points included new-onset AF and major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events.
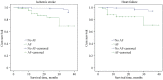
Results: Altogether, 322 patients were enrolled, with new-onset AF observed in 79 (24.5%) during their follow-up. Multivariable analysis identified four independent predictors of new-onset AF in elderly patients after pacemaker implantation: hypertension (HR = 3.040, 95% CI: 1.09-3.05, P = 0.00); age (HR = 1.966, 95% CI: 1.57-3.68, P = 0.01); left atrial enlargement (HR = 1.645, 95% CI: 1.05-1.25, P = 0.03); high ventricular pacing rate (HR = 1.137, 95% CI: 1.01-1.06, P = 0.01). Univariable analysis indicated that the CHA2DS2-VASc score was also a risk factor for AF (HR = 1.368, 95% CI: 1.178-1.589, P = 0.002), whereas multivariable regression analysis did not. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the risk for ischemic stroke was significantly higher in the new-onset AF group than in the non-AF group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Hypertension, age, left atrial enlargement, and high ventricular pacing rate were independent predictors of new-onset AF in elderly patients after implantation of a permanent pacemaker. New-onset AF increased the risk for ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Dual-chamber pacemaker; Elderly; Ischemic stroke.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pacemaker-detected atrial fibrillation burden and risk of ischemic stroke or thromboembolic events-A cohort study.Heart Lung. 2020 Jan-Feb;49(1):66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Heart Lung. 2020. PMID: 31376922
-
[Impact of atrial high-rate episodes on new onset of atrial fibrillation and all-cause mortality in elderly patients over 90 years old with dual-chamber pacemaker implantation].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2024 Oct 24;52(10):1148-1154. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20240615-00335. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39428363 Chinese.
-
The risk factors of new-onset atrial fibrillation after pacemaker implantation.Herz. 2021 Apr;46(Suppl 1):61-68. doi: 10.1007/s00059-019-04869-z. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Herz. 2021. PMID: 32107563 English.
-
Predictors and clinical impact of atrial fibrillation after pacemaker implantation in elderly patients treated with dual chamber versus ventricular pacing.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003 Oct;26(10):2000-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2003.00309.x. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003. PMID: 14516342 Clinical Trial.
-
Atrial pacing for the prevention and termination of atrial fibrillation.Am J Geriatr Cardiol. 2002 Nov-Dec;11(6):380-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1076-7460.2002.00072.x. Am J Geriatr Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 12417845 Review.
Cited by
-
Incidence of atrial high rate episodes after dual-chamber permanent pacemaker implantation and its clinical predictors.Indian Heart J. 2022 Nov-Dec;74(6):500-504. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2022.11.013. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Indian Heart J. 2022. PMID: 36460054 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Journal of Geriatric Cardiology over the course of a decade.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2020 Dec 28;17(12):733-739. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2020.12.001. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 33424940 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical impact of right ventricular pacing burden in patients with post-transcatheter aortic valve replacement permanent pacemaker implantation.Europace. 2023 Apr 15;25(4):1441-1450. doi: 10.1093/europace/euad025. Europace. 2023. PMID: 36794441 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ACEI/ARB or CCB use on atrial fibrillation in hypertensive patients following permanent pacemaker implantation.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jun 22;10:1191539. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1191539. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37424921 Free PMC article.
-
Association of furosemide or hydrochlorothiazide use with risk of atrial fibrillation post pacemaker implantation among elderly patients.Ann Transl Med. 2021 May;9(10):855. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-1792. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34164489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nielsen JC. Mortality and incidence of atrial fibrillation in paced patients. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002;13:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Wang M, Siu GW, Lee KL, et al. Effects of right low septalvs right atrial appendage pacing on atrial mechanical function and dyssynchrony in patients with sinus node dysfunction and pamxysmal atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2011;13:1268–1274. - PubMed
-
- Stambler BS, Ellenbogen KA, Orav EJ, et al. Predictors and clinical impact of atrial fibrillation after pacemaker implantation in elderly patients treated with dual chamber versus ventricular pacing. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003;26:2000–2007. - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann KE, Orav EJ, Lamas GA, et al. Atrial fibrillation and quality of life after pacemaker implantation for sick sinus syndrome: data from the Mode Selection Trial (MOST) Am Heart J. 2009;158:78–83. - PubMed
-
- Healey JS, Martin JL, Duncan A, et al. Pacemaker-detected atrial fibrillation in patients with pacemakers: prevalence, predictors, and current use of oral anticoagulation. Can J Cardiol. 2013;29:224–228. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources