Cutaneous Manifestations of Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases in Tunisian Children
- PMID: 30416697
- PMCID: PMC6223580
- DOI: 10.4084/MJHID.2018.065
Cutaneous Manifestations of Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases in Tunisian Children
Abstract
Skin manifestations are frequent among patients with primary immunodeficiency diseases (PIDs). Their prevalence varies according to the type of immunodeficiency. This review provides the reader with an up-to-date summary of the common dermatologic manifestations of PIDs among Tunisian children. We conducted a prospective study on two hundred and ninety children with immune deficiency. Demographic details (including age, sex, and consanguinity) with personal and family history were recorded. Special attention was paid to cutaneous manifestations. Dermatological involvements were grouped according to the etiology of their most prominent sign. Cutaneous manifestations were found in 164 patients (56.5%). They revealed the diagnosis of PIDs in 71 patients (24.5 %). The mean age at presentation was 21 months. Overall the most prominent cutaneous alterations were infectious. They accounted for 106 cases (36.55%). The most prevalent causes of cutaneous infections were bacterial: 93 cases (32.06%). Immuno-allergic skin diseases were among the common findings in our study. These include eczematous dermatitis found in 62 cases (21.38%). Malignancy related PIDs was seen in a boy with Wiskott Aldrich syndrome. He developed Kaposi's sarcoma at the age of 14 months. Cutaneous changes are common among children with PIDs. In pediatric patients with failure to thrive, chronic refractory systemic manifestations often present in other family members, recurrent cutaneous infections unresponsive to adequate therapy, atypical forms of eczematous dermatitis or unusual features should arouse the suspicion of PIDs and prompt specialized immunologic consultation should be made.
Keywords: Cutaneous infections; Cutaneous manifestations; Primary immunodeficiency; Wiskott Aldrich syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
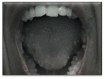
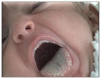


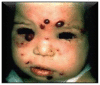
References
-
- Picard C, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Casanova JL, Chatila T, Conley ME, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, Holland SM, Klein C, Nonoyama S, Ochs HD, Oksenhendler E, Puck JM, Sullivan KE, Tang ML, Franco JL, Gaspar HB. Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: an Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee for Primary Immunodeficiency 2015. J Clin Immunol. 2015 Nov;35(8):696–726. doi: 10.1007/s10875-015-0201-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smitt JHS, Wulffraat NM, Kuijpers TW. The skin in primary immunodeficiency disorders. Eur J Dermatol. 2005;15:425–432. - PubMed
-
- Moin A, Farhoudi A, Moin M, Pourpak Z, Bazargan N. Cutaneous Manifestations of Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases in Children. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006;5:121–126. http://dx.doi.org/05.03/ijaai.121126. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

