Post-operative nonketotic hyperglycemic induced focal motor status epilepticus related to treatment with corticosteroids following standard anterior temporal lobectomy
- PMID: 30416961
- PMCID: PMC6215994
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebcr.2018.09.001
Post-operative nonketotic hyperglycemic induced focal motor status epilepticus related to treatment with corticosteroids following standard anterior temporal lobectomy
Abstract
•Complications from standard ATL are uncommon and the use of post-operative corticosteroids may reduce complications.•Following standard ATL, FMSE was present after treatment with corticosteroids that resolved after blood sugar control.•After epilepsy surgery, corticosteroids should be used cautiously in people with comorbid diabetes mellitus.
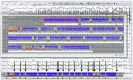
Figures

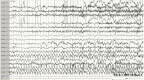
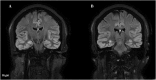
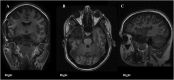
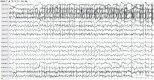
References
-
- Tatum W.O., 4th Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2012;29(5):356–365. - PubMed
-
- Wiebe S., Blume W.T., Girvin J.P., Eliasziw M. Effectives and Efficiency of Surgery for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Study Group. A randomized, controlled trial of surgery for temporal-lobe epilepsy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(5):311–318. - PubMed
-
- Wiebe S., Jette N. Pharmacoresistance and the role of surgery in difficult to treat epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012;8(12):669–677. - PubMed
-
- Engel J., Jr., Wiebe S., French J., Sperling M., Williamson P., Spencer D. Practice parameter: Temporal lobe and localized neocortical resections for epilepsy: Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology, in association with the American Epilepsy Society and the American Association of Neurological Surgeons. Neurology. 2003;60(4):538–547. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

