Contribution of CD137L to Sensory Hypersensitivity in a Murine Model of Neuropathic Pain
- PMID: 30417077
- PMCID: PMC6223109
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0218-18.2018
Contribution of CD137L to Sensory Hypersensitivity in a Murine Model of Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
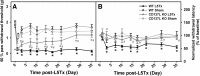
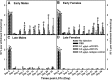
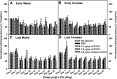
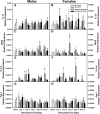
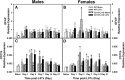
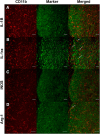
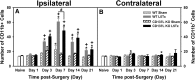
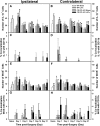
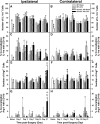
CD137L (4-1BBL) is a costimulatory molecule whose signaling can promote monocyte/macrophage functions; however, CD137L-mediated microglial response and its role in neuropathic pain remain unknown. We investigated CD137L following peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain using a spinal nerve L5 transection (L5Tx) murine model in both sexes. First, C57BL/6_CD137L knock-out (KO) mice displayed decreased mechanical and diminished heat hypersensitivity compared to wild-type (WT) controls, beginning on day 3 to up to day 35 post-L5Tx. Purified anti-mouse CD137L neutralizing monoclonal antibody (0.1 or 0.5 µg) was also used to identify CD137L's window of action in BALB/c mice. Anti-CD137L antibody was intrathecally administered either from day 0 (before surgery) to day 7 (early treatment), or from day 6 to 13 post-L5Tx (late treatment), and nociceptive thresholds were assessed before surgery to up to day 35 post-surgery. Early treatment with anti-CD137L reduced L5Tx-induced mechanical but not heat hypersensitivity, while later treatment did not alter either sensitivity. Pro- versus anti-inflammatory responses within the lumbar spinal cord following L5Tx were further evaluated via quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) in time-course studies. Following L5Tx, female CD137L KO mice did not show increased iNOS mRNA and had reduced numbers of IL-1β+ cells compared to WT. At 21 d post-surgery, CD137L KO mice had higher total numbers of arginase (Arg)-1+ cells and Arg-1+ microglia. Altogether, results indicate that spinal cord CD137L contributes to the development of peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain, which may be in part mediated through CD137L's modulation of the pro- and anti-inflammatory balance within the spinal cord.
Keywords: 4-1BBL; CD137L; L5 transection; microglia; mouse; neuropathic pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-nociceptive Role of CXCL1 in a Murine Model of Peripheral Nerve Injury-induced Neuropathic Pain.Neuroscience. 2018 Feb 21;372:225-236. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.12.048. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29309879 Free PMC article.
-
Differential lumbar spinal cord responses among wild type, CD4 knockout, and CD40 knockout mice in spinal nerve L5 transection-induced neuropathic pain.Mol Pain. 2012 Dec 18;8:88. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-88. Mol Pain. 2012. PMID: 23249743 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of microglial CD40 in the maintenance of mechanical hypersensitivity in a murine model of neuropathic pain.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Dec;39(12):3562-9. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939657. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19750482 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia and neuropathic pain.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Sep;12(6):768-72. doi: 10.2174/18715273113126660168. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 24047529 Review.
-
Microglia-Mediated Regulation of Neuropathic Pain: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms.Biol Pharm Bull. 2019;42(12):1959-1968. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00715. Biol Pharm Bull. 2019. PMID: 31787711 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the Expressions and m6A Methylation Modification Patterns of mRNAs and lncRNAs in a Spinal Cord Injury Rat Model.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):806-818. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04297-z. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38907070 Free PMC article.
-
CD137L, a driver of harmful inflammation in the nervous system.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Nov;18(11):2387-2388. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.371357. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 37282461 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rehabilitation: Neurogenic Bone Loss after Spinal Cord Injury.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 20;11(9):2581. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092581. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37761022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD137L Inhibition Ameliorates Hippocampal Neuroinflammation and Behavioral Deficits in a Mouse Model of Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy.Neuromolecular Med. 2023 Dec;25(4):616-631. doi: 10.1007/s12017-023-08764-z. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Neuromolecular Med. 2023. PMID: 37796401 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of CD137 Ligand Exacerbates Renal and Cutaneous but Alleviates Cerebral Manifestations in Lupus.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1411. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01411. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31297111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Pain Society (2018) Code of ethics. American Pain Society. Available at http://americanpainsociety.org/about-us/code-of-ethics/overview.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
