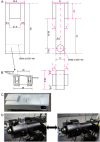
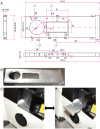
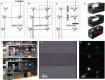
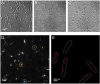
Conducting Multiple Imaging Modes with One Fluorescence Microscope
- PMID: 30417870
- PMCID: PMC6235614
- DOI: 10.3791/58320
Conducting Multiple Imaging Modes with One Fluorescence Microscope
Abstract
Fluorescence microscopy is a powerful tool to detect biological molecules in situ and monitor their dynamics and interactions in real-time. In addition to conventional epi-fluorescence microscopy, various imaging techniques have been developed to achieve specific experimental goals. Some of the widely used techniques include single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer (smFRET), which can report conformational changes and molecular interactions with angstrom resolution, and single-molecule detection-based super-resolution (SR) imaging, which can enhance the spatial resolution approximately ten to twentyfold compared to diffraction-limited microscopy. Here we present a customer-designed integrated system, which merges multiple imaging methods in one microscope, including conventional epi-fluorescent imaging, single-molecule detection-based SR imaging, and multi-color single-molecule detection, including smFRET imaging. Different imaging methods can be achieved easily and reproducibly by switching optical elements. This set-up is easy to adopt by any research laboratory in biological sciences with a need for routine and diverse imaging experiments at a reduced cost and space relative to building separate microscopes for individual purposes.
Similar articles
-
[Comparison and progress review of various super-resolution fluorescence imaging techniques].Se Pu. 2021 Oct;39(10):1055-1064. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.06015. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34505427 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
A Multicolor Single-Molecule FRET Approach to Study Protein Dynamics and Interactions Simultaneously.Methods Enzymol. 2016;581:487-516. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.08.024. Epub 2016 Oct 10. Methods Enzymol. 2016. PMID: 27793290
-
Multicolor Three-Dimensional Tracking for Single-Molecule Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Measurements.Anal Chem. 2018 May 15;90(10):6109-6115. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00244. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29671313
-
Super-Resolution Optical Lithography with DNA.Nano Lett. 2019 Sep 11;19(9):6035-6042. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01873. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Nano Lett. 2019. PMID: 31425652
-
Recent advances in super-resolution fluorescence imaging and its applications in biology.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Dec 20;40(12):583-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 23. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24377865 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Optical Contrast Agents for Medical Imaging: Fluorescent Probes and Molecular Imaging.J Imaging. 2025 Mar 18;11(3):87. doi: 10.3390/jimaging11030087. J Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40137199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinetic modeling reveals additional regulation at co-transcriptional level by post-transcriptional sRNA regulators.Cell Rep. 2021 Sep 28;36(13):109764. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109764. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34592145 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interactions between the RNA chaperone Hfq, small regulatory RNAs, and mRNAs in live bacterial cells.Elife. 2021 Feb 22;10:e64207. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64207. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33616037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lipson SG, Lipson H, Tannhauser DS. Optical physics. Cambridge, UK; New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 1995.
-
- Török P, Wilson T. Rigorous theory for axial resolution in confocal microscopes. Optics Communications. 1997;137(1-3):127–135.
-
- Klar TA, Hell SW. Subdiffraction resolution in far-field fluorescence microscopy. Optics Letters. 1999;24(14):954–956. - PubMed
-
- Hell SW, Wichmann J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Optics Letters. 1994;19(11):780–782. - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson MGL. Surpassing the lateral resolution limit by a factor of two using structured illumination microscopy. Journal of Microscopy. 2000;198(2):82–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials