A prospective clinical study of Primo-Lacto: A closed system for colostrum collection
- PMID: 30418987
- PMCID: PMC6231629
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206854
A prospective clinical study of Primo-Lacto: A closed system for colostrum collection
Abstract
Background: Colostrum is the first nutritional liquid that comes out of the breast during lactation. Colostrum collection can be challenging due to the small volume produced, and because breast pumps are not designed for colostrum collection. Besides pumping colostrum, the generally accepted practice is to use any available container to hand-express colostrum. Transfer between containers may lead to contamination, higher chance of infection and loss of colostrum. Our aim was to understand if a dedicated colostrum collection system (Primo-Lacto, Maternal Life, LLC, Palo Alto, CA) is more effective than standard hospital practice.
Methods: Mothers who delivered preterm infants < 34 weeks gestation and mothers with non-latching infants were approached within 24 hours of delivery. Surveys were distributed to participating patients (n = 67), and nurses or lactation consultants (n = 89). Mothers compared ease of use, their confidence level and satisfaction with the amount collected during standard practice vs. the colostrum collection system. Nurses or lactation consultants compared ease of use, differences in colostrum loss and time invested collecting. Quantitative data were analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed rank test and qualitative data were analyzed with grounded theory methods.
Results: For mothers, ease of use and confidence were significantly better when they used the colostrum collection system than when they used the standard collection procedure, and this difference was true for both hand and pump expression (p<0.01). Nurses and lactation consultants perceived that ease of use was better, and percent of colostrum lost was significantly less with the colostrum collection system for both hand and pump expression. The collection times were not significantly different between the colostrum collection system and standard practice.
Conclusion: The colostrum collection system is a tool to help facilitate successful colostrum collection and improve the experience both for clinicians and patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have read the journal's policy and have the following competing interests: JS invented the colostrum collection system (Primo-Lacto). This does not alter the authors' adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. The other authors of this study (AKC and HCL) have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
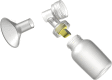



References
-
- Sridhar S, Arguello S, Lee H. Transition to Oral Feeding in Preterm Infants. NeoReviews. 2011;12(3):e141–e7. 10.1542/neo.12-3-e141 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

