Neutrophil-Mediated Proteolysis of Thrombospondin-1 Promotes Platelet Adhesion and String Formation
- PMID: 30419595
- PMCID: PMC6298231
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1675229
Neutrophil-Mediated Proteolysis of Thrombospondin-1 Promotes Platelet Adhesion and String Formation
Abstract
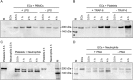
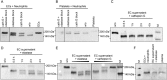
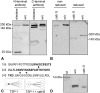
Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) is primarily expressed by platelets and endothelial cells (ECs) and rapidly released upon their activation. It functions in haemostasis as a bridging molecule in platelet aggregation, by promoting platelet adhesion to collagen and by protecting von Willebrand factor strings from degradation. In blood of patients undergoing surgery and in co-cultures of neutrophils with platelets or ECs, we observed proteolysis of the 185 kDa full-length TSP-1 to a 160-kDa isoform. We hypothesized that TSP-1 processing may alter its haemostatic properties. Selective enzyme inhibitors in co-cultures revealed that neutrophil proteases elastase and cathepsin G mediate TSP-1 processing. The cut site of cathepsin G was mapped to TSP-1 amino acids R237/T238 by Edman sequencing. Formation of neutrophil extracellular traps protected TSP-1 from complete degradation and promoted controlled processing to the 160-kDa isoform. Haemostatic properties were tested by platelet aggregation, adhesion, coagulation and string formation under flow. Platelets from TSP-1 deficient mice did not differ from wild-type in platelet aggregation but showed severe impairment of platelet adhesion to collagen and string formation under flow. Reconstitution experiments revealed that the 160-kDa TSP-1 isoform was markedly more potent than the 185-kDa full-length molecule in restoring function. Thus, TSP-1 processing by neutrophil proteases yields a 160-kDa isoform which shows enhanced potency to promote platelet adhesion and string formation. This finding reveals a novel mechanism of neutrophil-mediated thrombus formation and provides first evidence for the impact of TSP-1 proteolysis on its haemostatic properties.
Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart · New York.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
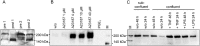

Similar articles
-
Role of thrombospondin-1 in control of von Willebrand factor multimer size in mice.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 14;279(20):21439-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313560200. Epub 2004 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14981081
-
Thrombospondin-1 controls vascular platelet recruitment and thrombus adherence in mice by protecting (sub)endothelial VWF from cleavage by ADAMTS13.Blood. 2006 Feb 1;107(3):955-64. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-12-4856. Epub 2005 Oct 4. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16204318 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin-1 promotes hemostasis through modulation of cAMP signaling in blood platelets.Blood. 2021 Feb 4;137(5):678-689. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020005382. Blood. 2021. PMID: 33538796
-
Platelet adhesion.Prog Hemost Thromb. 1984;7:211-88. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1984. PMID: 6397767 Review.
-
[Platelets: biochemistry and physiology].Hamostaseologie. 2008 Dec;28(5):289-98. Hamostaseologie. 2008. PMID: 19132160 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The Neutrophil Secretome as a Crucial Link between Inflammation and Thrombosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 17;22(8):4170. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084170. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33920656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Mediators of Platelet Activation: Focus on Atherosclerosis and COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 16;22(20):11170. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011170. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving cancer immunotherapy via co-delivering checkpoint blockade and thrombospondin-1 downregulator.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Aug;13(8):3503-3517. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.07.012. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37655330 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of thrombospondin-1 reduces glutathione activity and worsens acute liver injury during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 15;409:115323. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115323. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33176120 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 update: Covid-19-associated coagulopathy.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020 Jul;50(1):54-67. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02134-3. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020. PMID: 32415579 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gao A G, Lindberg F P, Finn M B, Blystone S D, Brown E J, Frazier W A. Integrin-associated protein is a receptor for the C-terminal domain of thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1996;271(01):21–24. - PubMed
-
- Baenziger N L, Brodie G N, Majerus P W. Isolation and properties of a thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1972;247(09):2723–2731. - PubMed

