Trimethylphosphate as a Methylating Agent for Cross Coupling: A Slow-Release Mechanism for the Methylation of Arylboronic Esters
- PMID: 30419749
- PMCID: PMC6827333
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b10076
Trimethylphosphate as a Methylating Agent for Cross Coupling: A Slow-Release Mechanism for the Methylation of Arylboronic Esters
Abstract
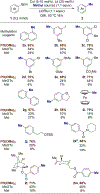
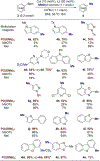
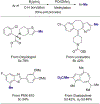
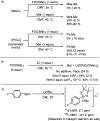
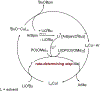
A methyl group on an arene, despite its small size, can have a profound influence on biologically active molecules. Typical methods to form a methylarene involve strong nucleophiles or strong and often toxic electrophiles. We report a strategy for a new, highly efficient, copper and iodide co-catalyzed methylation of aryl- and heteroarylboronic esters with the mild, nontoxic reagent trimethylphosphate, which has not been used previously in coupling reactions. We show that it reacts in all cases tested in yields that are higher than those of analogous copper-catalyzed reactions of MeOTs or MeI. The combination of C-H borylation and this methylation with trimethylphosphate provides a new approach to the functionalization of inert C-H bonds and is illustrated by late-stage methylation of four medicinally active compounds. In addition, reaction on a 200 mmol scale demonstrates reliability of this method. Mechanistic studies show that the reaction occurs by a slow release of methyl iodide by reaction of PO(OMe)3 with iodide catalyst, rather than the typical direct oxidative addition to a metal center. The low concentration of the reactive electrophile enables selective reaction with an arylcopper intermediate, rather than nucleophilic groups on the arylboronate, and binding of tert-butoxide to the boronate inhibits reaction of the electrophile with the tert-butoxide activator to form methyl ether.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson KE; Stamler D; Davis MD; Factor SA; Hauser RA; Isojärvi J; Jarskog LF; Jimenez-Shahed J; Kumar R; McEvoy JP; Ochudlo S; Ondo WG; Fernandez HH Lancet Psychiatry 2017, 4, 595–604. - PubMed
-
- Yan G; Borah AJ; Wang L; Yang M Adv. Synth. Catal 2015, 357, 1333–1350.
-
- Hall DG Boronic Acids: Preparation and Applications in Organic Synthesis and Medicine; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2005; pp 1 – 99.
-
- Gooßen L Appl. Organomet. Chem 2004, 18, 602–604.
- Yang CT; Zhang ZQ; Liu YC; Liu L Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2011, 50, 3904–3907. - PubMed

