In Vitro Anti-hepatitis B Virus Activity of 2',3'-Dideoxyguanosine
- PMID: 30421112
- PMCID: PMC6335223
- DOI: 10.1007/s12250-018-0065-7
In Vitro Anti-hepatitis B Virus Activity of 2',3'-Dideoxyguanosine
Abstract
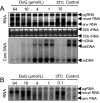
2',3'-dideoxyguanosine (DoG) has been demonstrated to inhibit duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) replication in vivo in a duck model of HBV infection. In the current study, the in vitro antiviral effects of DoG on human and animal hepadnaviruses were investigated. Our results showed that DoG effectively inhibited HBV, DHBV, and woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) replication in hepatocyte-derived cells in a dose-dependent manner, with 50% effective concentrations (EC50) of 0.3 ± 0.05, 6.82 ± 0.25, and 23.0 ± 1.5 μmol/L, respectively. Similar to other hepadnaviral DNA polymerase inhibitors, DoG did not alter the levels of intracellular viral RNA but induced the accumulation of a less-than-full-length viral RNA species, which was recently demonstrated to be generated by RNase H cleavage of pgRNA. Furthermore, using a transient transfection assay, DoG showed similar antiviral activity against HBV wild-type, 3TC-resistant rtA181V, and adefovir-resistant rtN236T mutants. Our results suggest that DoG has potential as a nucleoside analogue drug with anti-HBV activity.
Keywords: Antiviral; HBV; Hepatitis B; Nucleoside analogues; Woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Animal and Human Rights Statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vitro characterization of the anti-hepatitis B virus activity and cross-resistance profile of 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-fluoroguanosine.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Mar;50(3):955-61. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.3.955-961.2006. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16495257 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfamoylbenzamide derivatives inhibit the assembly of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsids.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(12):6931-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00582-13. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23576513 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of human and duck hepatitis B virus by 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-fluoroguanosine in vitro.Antiviral Res. 1998 Jan;37(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(97)00057-0. Antiviral Res. 1998. PMID: 9497073
-
Perspectives for the treatment of hepatitis B virus infections.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1999 Jul;12(2):81-95. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(99)00060-6. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1999. PMID: 10418752 Review.
-
Developments in Cell-Penetrating Peptides as Antiviral Agents and as Vehicles for Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acid Targeting Hepadnaviral Replication Pathway.Biomolecules. 2018 Jul 16;8(3):55. doi: 10.3390/biom8030055. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30013006 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Evolution of Cell Culture Systems to Study Hepatitis B Virus Pathogenesis and Antiviral Susceptibility.Viruses. 2025 Jul 29;17(8):1057. doi: 10.3390/v17081057. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40872772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn SH, Park YK, Park ES, Kim JH, Kim DH, Lim KH, Jang MS, Choe WH, Ko SY, Sung IK, Kwon SY, Kim KH. The impact of the hepatitis B virus polymerase rtA181T mutation on replication and drug resistance is potentially affected by overlapping changes in surface gene. J Virol. 2014;88:6518–6805. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00635-14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases Chinese Medical Association. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2010 version) Zhonghua Liuxing Bingxue Zazhi. 2011;32:405–415. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

