Attributable risk of Alzheimer's dementia attributed to age-related neuropathologies
- PMID: 30421454
- PMCID: PMC10128614
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.25380
Attributable risk of Alzheimer's dementia attributed to age-related neuropathologies
Abstract
Objective: The degree to which Alzheimer's versus other neuropathologies contribute to the risk of Alzheimer's dementia is unknown. We examined the risk of Alzheimer's dementia attributable to pathologic AD and 8 other neuropathologies.
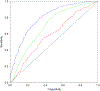
Methods: Participants (n = 1,161) came from 2 clinical-pathological studies of aging. Multivariable logistic regression models examined associations of 8 neuropathological indices with Alzheimer's dementia and quantified the percentage of cases attributable to each. Furthermore, because some dementia cases are not driven by common neuropathologies, we re-estimated the attributable risks after empirically adjusting for such cases.
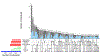
Results: Of 1,161 persons, 512 (44.1%) had Alzheimer's dementia at time of death. With the exception of microinfarcts, all neuropathological indices were independently associated with greater odds of Alzheimer's dementia. Two hundred ten (41.0%) Alzheimer's dementia cases were attributable to pathological AD. Separately, 8.9% were attributable to macroscopic infarcts, 10.8% to Lewy bodies, 5.2% to hippocampal sclerosis, 11.7% to transactive response DNA-binding protein 43, 8.1% to cerebral amyloid angiopathy, 6.0% to atherosclerosis, and 5.2% to arteriolosclerosis. A total of 83.3% of cases were attributable to all 8 indices combined. However, after further adjustment for cases driven by other factors, a total of 67.5% of cases were attributable to all 8 neuropathologic indices combined.
Interpretation: Pathological AD accounts for a considerable percentage of Alzheimer's dementia cases, but multiple other neuropathologies also contribute. In total, just over two-thirds of Alzheimer's dementia cases are attributable to common age-related neuropathologies, suggesting that other disease and resilience factors are important. ANN NEUROL 2019;85:114-124.
© 2018 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential Conflicts of Interest
Nothing to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
To what degree is late life cognitive decline driven by age-related neuropathologies?Brain. 2021 Aug 17;144(7):2166-2175. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab092. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33742668 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease frequency peaks in the tenth decade and is lower afterwards.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019 Jul 3;7(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0752-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31269985 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in Alzheimer's disease and common neuropathologies of aging.Acta Neuropathol. 2018 Dec;136(6):887-900. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1920-1. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. PMID: 30334074 Free PMC article.
-
What is 'Alzheimer's disease'? The neuropathological heterogeneity of clinically defined Alzheimer's dementia.Curr Opin Neurol. 2021 Apr 1;34(2):237-245. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000912. Curr Opin Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33591030 Review.
-
Sex differences in mixed neuropathologies in community-dwelling older adults.Brain Res. 2019 Sep 15;1719:11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.05.028. Epub 2019 May 22. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31128096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CD33 and SHP-1/PTPN6 Interaction in Alzheimer's Disease.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 13;15(9):1204. doi: 10.3390/genes15091204. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336795 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Preventive Trial for Alzheimer's Disease: MIND-ADmini Pilot Trial Study Design and Progress.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2022;9(1):30-39. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2022.4. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 35098971 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Open peer review commentary on building clinically relevant outcomes across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2021 Jun 26;7(1):e12192. doi: 10.1002/trc2.12192. eCollection 2021. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2021. PMID: 34195351 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Alzheimer's Amyloid Hypothesis and Antibody Therapy: Melting Glaciers?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 31;25(7):3892. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073892. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neurovasculome: Key Roles in Brain Health and Cognitive Impairment: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association.Stroke. 2023 Jun;54(6):e251-e271. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000431. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Stroke. 2023. PMID: 37009740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2017. Facts and figures. www.alz.org/facts. Accessed April 1, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

