Non-invasive imaging in dermatology and the unique potential of raster-scan optoacoustic mesoscopy
- PMID: 30422337
- PMCID: PMC6563473
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.15342
Non-invasive imaging in dermatology and the unique potential of raster-scan optoacoustic mesoscopy
Abstract
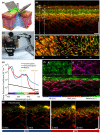
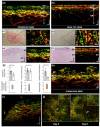
In recent years, several non-invasive imaging methods have been introduced to facilitate diagnostics and therapy monitoring in dermatology. The microscopic imaging methods are restricted in their penetration depth, while the mesoscopic methods probe deeper but provide only morphological, not functional, information. 'Raster-scan optoacoustic mesoscopy' (RSOM), an emerging new imaging technique, combines deep penetration with contrast based on light absorption, which provides morphological, molecular and functional information. Here, we compare the capabilities and limitations of currently available dermatological imaging methods and highlight the principles and unique abilities of RSOM. We illustrate the clinical potential of RSOM, in particular for non-invasive diagnosis and monitoring of inflammatory and oncological skin diseases.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures
References
-
- Koehler MJ, Speicher M, Lange‐Asschenfeldt S et al Clinical application of multiphoton tomography in combination with confocal laser scanning microscopy for in vivo evaluation of skin diseases. Exp Dermatol 2011; 20: 589–594. - PubMed
-
- Ulrich M. Konfokale laserscanmikroskopie. Der Hautarzt 2015; 66: 504–510. - PubMed
-
- Themstrup L, de Carvalho N, Nielsen SM et al In vivo differentiation of common basal cell carcinoma subtypes by microvascular and structural imaging using dynamic optical coherence tomography. Exp Dermatol 2018; 27: 156–165. - PubMed
-
- Ntziachristos V. Going deeper than microscopy: the optical imaging frontier in biology. Nat Methods 2010; 7: 603–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

