PEGylated IL-10 (Pegilodecakin) Induces Systemic Immune Activation, CD8+ T Cell Invigoration and Polyclonal T Cell Expansion in Cancer Patients
- PMID: 30423297
- PMCID: PMC8098754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.10.007
PEGylated IL-10 (Pegilodecakin) Induces Systemic Immune Activation, CD8+ T Cell Invigoration and Polyclonal T Cell Expansion in Cancer Patients
Abstract
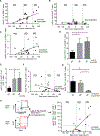
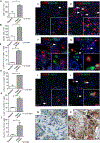
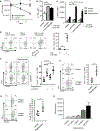
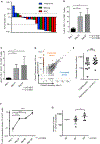
Tumor-reactive T cell exhaustion prevents the success of immune therapies. Pegilodecakin activates intratumoral CD8+ T cells in mice and induces objective tumor responses in patients. Here we report that pegilodecakin induces hallmarks of CD8+ T cell immunity in cancer patients, including elevation of interferon-γ and GranzymeB, expansion and activation of intratumoral CD8+ T cells, and proliferation and expansion of LAG-3+ PD-1+ CD8+ T cells. On pegilodecakin, newly expanded T cell clones, undetectable at baseline, become 1%-10% of the total T cell repertoire in the blood. Elevation of interleukin-18, expansion of LAG-3+ PD-1+ T cells and novel T cell clones each correlated with objective tumor responses. Combined pegilodecakin with anti-PD-1 increased the expansion of LAG-3+ PD-1+ CD8+ T cells.
Keywords: AM0010; CD8(+) T cell; IL-10; PEGylated Interleukin 10; T cell invigoration; Th1; clinical trial; clonal expansion; clonality; pegilodecakin.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Afanasiev OK, Yelistratova L, Miller N, Nagase K, Paulson K, Iyer JG, Ibrani D, Koelle DM, and Nghiem P. (2013). Merkel polyomavirus-specific T cells fluctuate with merkel cell carcinoma burden and express therapeutically targetable PD-1 and Tim-3 exhaustion markers. Clin. Cancer Res. 19, 5351–5360. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berg DJ, Davidson N, Kuhn R, Muller W, Menon S, Holland G, Thompson-Snipes L, Leach MW, and Rennick D. (1996). Enterocolitis and colon cancer in interleukin-10-deficient mice are associated with aberrant cytokine production and CD4(+) TH1-like responses. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 1010–1020. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bromberg J, and Darnell JE Jr. (2000). The role of STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular function. Oncogene 19, 2468–2473. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

