Role of Overexpressed Transcription Factor FOXO1 in Fatal Cardiovascular Septal Defects in Patau Syndrome: Molecular and Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 30423812
- PMCID: PMC6274780
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113547
Role of Overexpressed Transcription Factor FOXO1 in Fatal Cardiovascular Septal Defects in Patau Syndrome: Molecular and Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
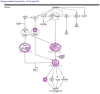
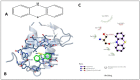
Patau Syndrome (PS), characterized as a lethal disease, allows less than 15% survival over the first year of life. Most deaths owe to brain and heart disorders, more so due to septal defects because of altered gene regulations. We ascertained the cytogenetic basis of PS first, followed by molecular analysis and docking studies. Thirty-seven PS cases were referred from the Department of Pediatrics, King Abdulaziz University Hospital to the Center of Excellence in Genomic Medicine Research, Jeddah during 2008 to 2018. Cytogenetic analyses were performed by standard G-band method and trisomy13 were found in all the PS cases. Studies have suggested that genes of chromosome 13 and other chromosomes are associated with PS. We, therefore, did molecular pathway analysis, gene interaction, and ontology studies to identify their associations. Genomic analysis revealed important chr13 genes such as FOXO1, Col4A1, HMGBB1, FLT1, EFNB2, EDNRB, GAS6, TNFSF1, STARD13, TRPC4, TUBA3C, and TUBA3D, and their regulatory partners on other chromosomes associated with cardiovascular disorders, atrial and ventricular septal defects. There is strong indication of involving FOXO1 (Forkhead Box O1) gene-a strong transcription factor present on chr13, interacting with many septal defects link genes. The study was extended using molecular docking to find a potential drug lead for overexpressed FOXO1 inhibition. The phenothiazine and trifluoperazine showed efficiency to inhibit overexpressed FOXO1 protein, and could be potential drugs for PS/trisomy13 after validation.
Keywords: FOXO1; Patau Syndrome; and drug design; bioinformatics; cytogenetics; molecular docking; molecular pathways; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cytogenetics of Spindle Cell/Pleomorphic Lipomas: Karyotyping and FISH Analysis of 31 Tumors.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2018 May-Jun;15(3):193-200. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20077. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29695401 Free PMC article.
-
[Fetal atrioventricular septal defect associated with Patau and Edwards syndromes, as well as trisomy 22].Orv Hetil. 1998 May 3;139(18):1087-9. Orv Hetil. 1998. PMID: 9608772 Hungarian.
-
Phenotypic variability in Patau syndrome.Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2013 Apr-Jun;117(2):321-7. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2013. PMID: 24340511
-
A global perspective on FOXO1 in lipid metabolism and lipid-related diseases.Prog Lipid Res. 2017 Apr;66:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Prog Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28392404 Review.
-
The regulation of FOXO1 and its role in disease progression.Life Sci. 2018 Jan 15;193:124-131. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.11.030. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29158051 Review.
Cited by
-
A Six-Year-Old Child With Mosaic Trisomy 13.Cureus. 2021 Sep 28;13(9):e18346. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18346. eCollection 2021 Sep. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34722094 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting HR Repair as a Synthetic Lethal Approach to Increase DNA Damage Sensitivity by a RAD52 Inhibitor in BRCA2-Deficient Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 23;22(9):4422. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094422. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33922657 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping integral cell-type-specific interferon-induced gene regulatory networks (GRNs) involved in systemic lupus erythematosus using systems and computational analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 18;11(1):e41342. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41342. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39844998 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals Pathogenic SIRT1 Variant in Brain Arteriovenous Malformation: A Case Report.Genes (Basel). 2022 Sep 21;13(10):1689. doi: 10.3390/genes13101689. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292575 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulation: Molecules, Involved Mechanisms, and Misregulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 14;20(6):1281. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061281. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30875728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duarte A.C., Menezes A.I., Devens E.S., Roth J.M., Garcias G.L., Martino-Roth M.G. Patau syndrome with a long survival. A case report. Genet. Mol. Res. 2004;3:288–292. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

