Efficacy of antifungal drugs in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
- PMID: 30425538
- PMCID: PMC6203166
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S175588
Efficacy of antifungal drugs in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Antifungal drugs are used frequently in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), but have shown controversial results. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of different antifungal drugs in the treatment of VVC and to provide an evidence-based reference for clinical use.
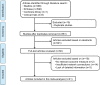
Methods: The published studies on the effectiveness of antifungal drugs in the treatment of VVC (up to April 2018) were retrieved from PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and Clini-calTrials.gov. We sifted through the literature according to Patients, Interventions, Comparisons and Outcomes principle, extracted data on the basic characteristics of the study, and evaluated the quality of included studies. We used R software for statistical analysis.
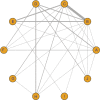
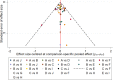
Results: In total, 41 randomized controlled trials were included in this meta-analysis. The relative risk of VVC associated with ten drugs, including placebo, fluconazole, clotrimazole, miconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, econazole, butoconazole, terbinafine, and terconazole, was analyzed. The following drugs appeared to show more efficacy than placebo in the treated patients: fluconazole (OR =6.45, 95% CrI 4.42-9.41), clotrimazole (OR =2.99, 95% CrI 1.61-5.55), miconazole (OR =5.96, 95% CrI 3.17-11.2), itraconazole (OR =2.29, 95% CrI 1.21-4.33), ketoconazole (OR =2.40, 95% CrI 1.55-3.71), butoconazole (OR =1.18, 95% CrI 1.06-1.31), and terconazole (OR =5.60, 95% CrI 2.78-11.3). The value of surface under the cumulative ranking curve of each drug was as follows: placebo (0.5%), fluconazole (91.5%), clotrimazole (61.8%), miconazole (33.8%), itraconazole (50.5%), ketoconazole (42.8%), econazole (46.8%), butoconazole (82.2%), terbinafine (20.9%), and terconazole (65.0%).
Conclusion: Antifungal drugs are effective in the treatment of VVC. Fluconazole appeared to be the best drug for the treatment of VVC according to our analysis.
Keywords: antifungal drugs; network meta-analysis; randomized controlled trials; vulvovaginal candidiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Nwadioha SI, Nwokedi EO, Egesie J, Enejuo H. Vaginal candidiasis and its risk factors among women attending a Nigerian teaching hospital. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2013;20(1):20–23. - PubMed
-
- Gonçalves B, Ferreira C, Alves CT, Henriques M, Azeredo J, Silva S. Vulvovaginal candidiasis: Epidemiology, microbiology and risk factors. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42(6):905–927. - PubMed
-
- Mikamo H, Kawazoe K, Sato Y, Hayasaki Y, Tamaya T. Comparative study on the effectiveness of antifungal agents in different regimens against vaginal candidiasis. Chemotherapy. 1998;44(5):364–368. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

