Effects of Digeda-4 Decoction on the CYP450 Activities in Rats Using a Cocktail Method by HPLC
- PMID: 30426002
- PMCID: PMC6218799
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1415082
Effects of Digeda-4 Decoction on the CYP450 Activities in Rats Using a Cocktail Method by HPLC
Abstract
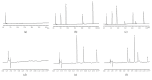
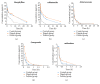
Digeda-4 decoction is a traditional Mongolian medicine; its effects on cytochrome (CYP) enzymes are still unclear. CYP450 isoenzymes are the main drug metabolic enzymes, and their activities may be induced or inhibited by certain drugs, which lead to drug interactions in clinical use. Effects of Digeda-4 decoction on the activities of CYP450 subtype enzymes CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2E1, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4 in rats were studied by cocktail method, and the pharmacokinetic parameters of five specific probe drugs (theophylline, tolbutamide, chlorzoxazone, omeprazole, and midazolam) were calculated by DAS software; changes of parameters can be used to evaluate the effects of Digeda-4 decoction on enzyme activities. The experimental rats were divided into three groups: control group, Digeda group, and positive group. Rats in Digeda group were given Digeda-4 decoction through continuous gavage for 14 days. After fasting for 12 hours, the mixed probes drug solution was injected into the tail vein; the blood samples were collected through the orbital vein at different time points. The concentrations of probe drugs in rat plasma were measured by HPLC. Compared with the control group, the half-life time (t1/2) of the pharmacokinetic parameters of theophylline, tolbutamide, omeprazole, and midazolam was prolonged, the area under the curve (AUC) increased, and the plasma clearance (CL) decreased in the Digeda group. Continuous gavage administration for 14 days may inhibit the activities of CYP450 subtype enzymes CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4 of rats. Herb-drug interaction should be noted between Digeda-4 decoction and the drugs metabolized by CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

