Apalutamide and its use in the treatment of prostate cancer
- PMID: 30426794
- PMCID: PMC6391625
- DOI: 10.2217/fon-2018-0546
Apalutamide and its use in the treatment of prostate cancer
Abstract
High-risk nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer is a lethal disease that previously lacked clear treatment options. Progression to bone metastases is associated with significant morbidity and high cost. Apalutamide, an androgen receptor inhibitor, has substantial clinical response in nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Apalutamide + androgen deprivation therapy is well tolerated and improves metastasis-free survival, progression-free survival and time to symptomatic progression, and is associated with a favorable trend of improved overall survival. Future research is needed to elucidate mechanisms of resistance to treatment with androgen signaling inhibitors.
Keywords: androgen signaling inhibitor; apalutamide; castration-resistant prostate cancer; nonmetastatic; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
EJ Small has received honoraria from Janssen. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures

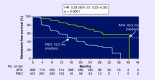
References
-
- Data S. Cancer stat facts: prostate cancer. 2015 https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html
-
- Magnan S, Zarychanski R, Pilote L, et al. Intermittent vs continuous androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1(9):1261–1269. - PubMed
-
•• A systematic review of androgen deprivation therapy treatment duration in prostate cancer.
-
- NCCN. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) Prostate Cancer. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate.pdf - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
