Discovery of a novel DNA polymerase inhibitor and characterization of its antiproliferative properties
- PMID: 30427259
- PMCID: PMC6422523
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1529126
Discovery of a novel DNA polymerase inhibitor and characterization of its antiproliferative properties
Abstract
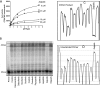
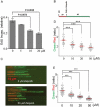
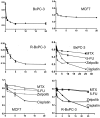
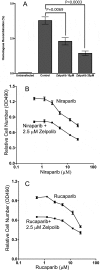
Chromosomal duplication is targeted by various chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of cancer. However, there is no specific inhibitor of DNA polymerases that is viable for cancer management. Through structure-based in silico screening of the ZINC database, we identified a specific inhibitor of DNA polymerase δ. The discovered inhibitor, Zelpolib, is projected to bind to the active site of Pol δ when it is actively engaged in DNA replication through interactions with DNA template and primer. Zelpolib shows robust inhibition of Pol δ activity in reconstituted DNA replication assays. Under cellular conditions, Zelpolib is taken up readily by cancer cells and inhibits DNA replication in assays to assess global DNA synthesis or single-molecule bases by DNA fiber fluorography. In addition, we show that Zelpolib displays superior antiproliferative properties to methotrexate, 5-flourouracil, and cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer cell line, pancreatic cancer cell line and platinum-resistant pancreatic cancer cell line. Pol δ is not only involved in DNA replication, it is also a key component in many DNA repair pathways. Pol δ is the key enzyme responsible for D-loop extension during homologous recombination. Indeed, Zelpolib shows robust inhibition of homologous recombination repair of DNA double-strand breaks and induces "BRCAness" in HR-proficient cancer cells and enhances their sensitivity to PARP inhibitors.
Keywords: DNA polymerase delta; DNA repair; DNA replication; PARP inhibitor; olaparib; polymerase inhibitor.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Loss of the p12 subunit of DNA polymerase delta leads to a defect in HR and sensitization to PARP inhibitors.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Jan;73:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.11.003. Epub 2018 Nov 13. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 30470508 Free PMC article.
-
RAD6B is a major mediator of triple negative breast cancer cisplatin resistance: Regulation of translesion synthesis/Fanconi anemia crosstalk and BRCA1 independence.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Jan 1;1866(1):165561. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165561. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 31639439 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting the MCM8-9 complex selectively sensitizes cancer cells to cisplatin and olaparib.Cancer Sci. 2019 Mar;110(3):1044-1053. doi: 10.1111/cas.13941. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30648820 Free PMC article.
-
[Cancer therapy by PARP inhibitors].Nihon Rinsho. 2015 Aug;73(8):1330-5. Nihon Rinsho. 2015. PMID: 26281686 Review. Japanese.
-
Two forms of human DNA polymerase δ: Who does what and why?DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Sep;81:102656. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102656. Epub 2019 Jul 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31326365 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploiting DNA Replication Stress as a Therapeutic Strategy for Breast Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 1;10(11):2775. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112775. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision Oncology with Drugs Targeting the Replication Stress, ATR, and Schlafen 11.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 14;13(18):4601. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184601. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP inhibitor resistance: the underlying mechanisms and clinical implications.Mol Cancer. 2020 Jun 20;19(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01227-0. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32563252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision medicine in pancreatic cancer: treating every patient as an exception.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct;4(10):805-810. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30175-X. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31511204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging actionable targets to treat therapy-resistant colorectal cancers.Cancer Drug Resist. 2022 Jan 4;5(1):36-63. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2021.96. eCollection 2022. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35582524 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Karran P. Mechanisms of tolerance to DNA damaging therapeutic drugs. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22:1931–1937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
