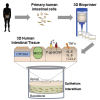
Bioprinted 3D Primary Human Intestinal Tissues Model Aspects of Native Physiology and ADME/Tox Functions
- PMID: 30428372
- PMCID: PMC6135981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.03.015
Bioprinted 3D Primary Human Intestinal Tissues Model Aspects of Native Physiology and ADME/Tox Functions
Abstract
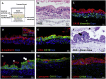
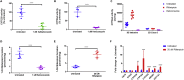
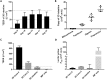
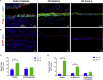
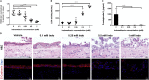
The human intestinal mucosa is a critical site for absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME)/Tox studies in drug development and is difficult to recapitulate in vitro. Using bioprinting, we generated three-dimensional (3D) intestinal tissue composed of human primary intestinal epithelial cells and myofibroblasts with architecture and function to model the native intestine. The 3D intestinal tissue demonstrates a polarized epithelium with tight junctions and specialized epithelial cell types and expresses functional and inducible CYP450 enzymes. The 3D intestinal tissues develop physiological barrier function, distinguish between high- and low-permeability compounds, and have functional P-gp and BCRP transporters. Biochemical and histological characterization demonstrate that 3D intestinal tissues can generate an injury response to compound-induced toxicity and inflammation. This model is compatible with existing preclinical assays and may be implemented as an additional bridge to clinical trials by enhancing safety and efficacy prediction in drug development.
Keywords: Bioengineering; In Vitro Toxicology Including 3D Culture; Tissue Engineering.
Copyright © 2018 Organovo Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Allen J.D., van Loevezijn A., Lakhai J.M., van der Valk M., van Tellingen O., Reid G., Schellens J.H., Koomen G.J., Schinkel A.H. Potent and specific inhibition of the breast cancer resistance protein multidrug transporter in vitro and in mouse intestine by a novel analogue of fumitremorgin C. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002;1:417–425. - PubMed
-
- Alqahtani S., Mohamed L.A., Kaddoumi A. Experimental models for predicting drug absorption and metabolism. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013;9:1241–1254. - PubMed
-
- Bentz J., O’Connor M.P., Bednarczyk D., Coleman J.A., Lee C., Palm J., Pak Y.A., Perloff E.S., Reyner E., Balimane P. Variability in p-glycoprotein inhibitory potency (ic(50)) using various in vitro experimental systems: implications for universal digoxin drug-drug interaction risk assessment decision criteria. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013;41:1347–1366. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhatia S.N., Ingber D.E. Microfluidic organs-on-chips. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014;32:760–772. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

