Protocol for evaluating the effects of a foot-ankle therapeutic exercise program on daily activity, foot-ankle functionality, and biomechanics in people with diabetic polyneuropathy: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 30428863
- PMCID: PMC6236874
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-018-2323-0
Protocol for evaluating the effects of a foot-ankle therapeutic exercise program on daily activity, foot-ankle functionality, and biomechanics in people with diabetic polyneuropathy: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) negatively affects foot and ankle function (strength and flexibility), which itself affects the daily physical activity and quality of life of patients. A physical therapy protocol aiming to strengthen the intrinsic and extrinsic foot muscles and increase flexibility may be a promising approach to improve lower-extremity function, prevent further complications, and improve autonomy for daily living activities in these patients. Thus, the inclusion of a specific foot-related exercises focused on the main musculoskeletal impairments may have additional effects to the conventional interventions in the diabetic foot.
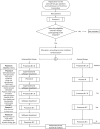
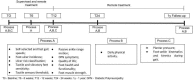
Methods/design: A prospective, parallel-group, outcome-assessor blinded, randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted in 77 patients with DPN who will be randomly allocated to usual care (control arm) or usual care with supervised foot-ankle exercises aiming to increase strengh and flexibility twice a week for 12 weeks and remotely supervised foot-ankle exercises for a year through a web software. Patients will be evaluated 5 times in a 1 year period regarding daily physical activity level, self-selected and fast gait speeds (primary outcomes), foot ulcer incidence, ulcer risk classification, neuropathy testing, passive ankle range of motion, quality of life, foot health and functionality, foot muscle strength, plantar pressure, and foot-ankle kinematics and kinetics during gait.
Discussion: This study aims to assess the effect of a foot-ankle strength and flexibility program on a wide range of musculoskeletal, activity-related, biomechanical, and clinical outcomes in DPN patients. We intend to demonstrate evidence that the year-long training program is effective in increasing gait speed and daily physical activity level and in improving quality of life; foot strength, functionality, and mobility; and biomechanics while walking. The results will be published as soon as they are available.
Trial registration: This study has been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov as NCT02790931 (June 6, 2016) under the name "Effects of foot muscle strengthening in daily activity in diabetic neuropathic patients".
Keywords: Clinical trial; Diabetic foot; Diabetic neuropathies; Exercise; Foot ulcer; Physical therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Medicine of the University of São Paulo (Protocol 1.464.870). All patients will be asked for written informed consent according to the standard forms and the researcher will obtain them.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of all images was obtained from the models.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Sartor CD, Hasue RH, Cacciari LP, et al. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. Rome: Physical therapy, speech and occupational therapy Dept, School of Medicine, University of São Paulo, 51, Cidade Universitária, São Paulo, SP, BrazilDepartment of technology and health, Italian National Institute of health; 2014. Effects of strengthening, stretching and functional training on foot function in patients with diabetic neuropathy: results of a randomized controlled trial; p. 137. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical