Efficacy and safety of low-dose Sirolimus in Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- PMID: 30428897
- PMCID: PMC6236936
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0946-8
Efficacy and safety of low-dose Sirolimus in Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
Abstract
Background: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis is a rare disease caused by unregulated activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway. Sirolimus showed efficacy in a phase 3 trial of patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis, but the optimal dose remains unclear.
Methods: We investigated the efficacy and safety of low-dose compared with conventional-dose sirolimus. Clinical data of 39 patients with lymphangioleiomyomatosis (mean age, 34.8 years; median treatment period, 29.6 months) who received sirolimus were retrospectively reviewed. Low-dose sirolimus was defined as any dose that maintained mean blood trough levels lower than those maintained with conventional doses (5-15 ng/mL).
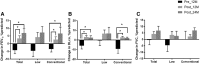
Results: Fifty-one percent of patients received low-dose therapy. The rate of decline in lung function decreased after treatment in the whole group (forced expiratory volume in 1 s [FEV1], - 0.12 ± 0.47 [before] vs. 0.24 ± 0.48% predicted/month [after], p = 0.027; diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide [DLco], - 0.33 ± 0.61 vs. 0.03 ± 0.26% predicted/month, p = 0.006) compared with before treatment. In the low-dose group, the rate of decline in FEV1 (- 0.08 ± 0.38 [before] vs. 0.19 ± 0.51% predicted/month [after], p = 0.264) and DLco (-0.13 ± 0.62 vs. 0.02 ± 0.28% predicted/month, p = 0.679) showed a numeric trend towards improvement after treatment; however, the conventional-dose group showed significant improvement in FEV1 (- 0.26 ± 0.54 [before] vs. 0.22 ± 0.38 [after] % predicted/month, p = 0.024) and DLco (- 0.55 ± 0.58 vs. 0.04 ± 0.25% predicted/month, p = 0.002) after treatment. Adverse events (AEs) occurred in 89.7% of patients and the most common AEs was hypercholesterolaemia (43.6%), followed by stomatitis (35.9%). The occurrences of AE were similar between the low- and conventional-dose groups (85.0% vs. 94.7%, p = 0.605).
Conclusions: Low-dose sirolimus may stabilise lung function decline in lymphangioleiomyomatosis patients, but its efficacy appears to be inferior to that of conventional-dose sirolimus.
Keywords: Low dose; Lymphangioleiomyomatosis; Respiratory function tests; Sirolimus; Treatment outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Asan Medical Center Institutional Review Board (2016–0480).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

