Long non-coding RNA ABHD11-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer development through regulation of miR-133a/SOX4 axis
- PMID: 30429229
- PMCID: PMC6294614
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20181386
Long non-coding RNA ABHD11-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer development through regulation of miR-133a/SOX4 axis
Abstract
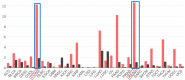
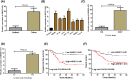
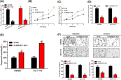
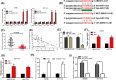
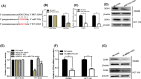
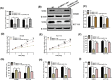
Recently, lncRNA has been verified to regulate the development and progression of tumor. LncRNA ABHD11-AS1 has been proven to serve as an oncogene in several cancers. However, the role of ABHD11-AS1 in colorectal cancer remains totally unknown. In the present study, qRT-PCR assay revealed that ABHD11-AS1 expression was markedly higher in colorectal cancer tissues and cell lines. In addition, patients who displayed overexpression of ABHD11-AS1 showed a significantly poorer progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) by Kaplan-Meier analysis. Loss-of-function experiments suggested that silencing of ABHD11-AS1 expression could significantly reduce the proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells, and increase cell apoptosis. Moreover, bioinformatics analysis, biotin pull-down assay, luciferase reporter assay, and RIP assay disclosed that ABHD11-AS1 straightly interacted with miR-133a. We also found that SOX4 was a downstream target of miR-133a and ABHD11-AS1 subsequently exerted its biological effects via modulating the expression of SOX4 in colorectal cancer cells. Collectively, these findings manifested that the ABHD11-AS1/miR-133a/SOX4 axis may be a cogitable and promising therapeutic target for colorectal cancer.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; large intervening non-coding RNA; microRNA; tumorigenesis.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association between long noncoding RNA ABHD11-AS1 and malignancy prognosis: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):1083. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12866-7. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39223500 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 sponges miR-194 to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via up-regulating TGFα.Cancer Biomark. 2018;23(1):145-156. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181503. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 30010111
-
Long noncoding RNA ABHD11-AS1 promote cells proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer via regulating the miR-1254-WNT11 pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jul;234(7):12070-12079. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27877. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30537177
-
Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 induced progression of ovarian cancer via regulating miR-130a-5p/SOX4 axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Apr;24(7):4275-4285. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15088. Epub 2020 Mar 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32135030 Free PMC article.
-
FEZF1-AS1: a novel vital oncogenic lncRNA in multiple human malignancies.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jun 25;39(6):BSR20191202. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191202. Print 2019 Jun 28. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31175144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Buffalo long non-coding RNA gene11007 promotes myoblasts proliferation.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Aug 5;9:857044. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.857044. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36032282 Free PMC article.
-
The association between long noncoding RNA ABHD11-AS1 and malignancy prognosis: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):1083. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12866-7. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39223500 Free PMC article.
-
α/β-Hydrolase Domain (ABHD) Inhibitors as New Potential Therapeutic Options against Lipid-Related Diseases.J Med Chem. 2021 Jul 22;64(14):9759-9785. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00624. Epub 2021 Jul 2. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34213320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
lncRNA PCGEM1 Regulates the Progress of Colorectal Cancer through Targeting miR-129-5p/SOX4.Dis Markers. 2022 Sep 20;2022:2876170. doi: 10.1155/2022/2876170. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36193492 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in understanding the role of lncRNA in programmed cell death.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Feb 8;7(1):30. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00407-1. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 33558499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

