DksA-DnaJ redox interactions provide a signal for the activation of bacterial RNA polymerase
- PMID: 30429329
- PMCID: PMC6294903
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1813572115
DksA-DnaJ redox interactions provide a signal for the activation of bacterial RNA polymerase
Abstract
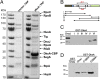
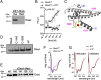
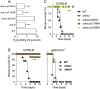
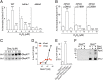
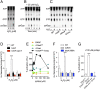
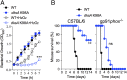
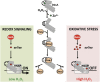
RNA polymerase is the only known protein partner of the transcriptional regulator DksA. Herein, we demonstrate that the chaperone DnaJ establishes direct, redox-based interactions with oxidized DksA. Cysteine residues in the zinc finger of DksA become oxidized in Salmonella exposed to low concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The resulting disulfide bonds unfold the globular domain of DksA, signaling high-affinity interaction of the C-terminal α-helix to DnaJ. Oxidoreductase and chaperone activities of DnaJ reduce the disulfide bonds of its client and promote productive interactions between DksA and RNA polymerase. Simultaneously, guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp), which is synthesized by RelA in response to low concentrations of H2O2, binds at site 2 formed at the interface of DksA and RNA polymerase and synergizes with the DksA/DnaJ redox couple, thus activating the transcription of genes involved in amino acid biosynthesis and transport. However, the high concentrations of ppGpp produced by Salmonella experiencing oxidative stress oppose DksA/DnaJ-dependent transcription. Cumulatively, the interplay of DksA, DnaJ, and ppGpp on RNA polymerase protects Salmonella from the antimicrobial activity of the NADPH phagocyte oxidase. Our research has identified redox-based signaling that activates the transcriptional activity of the RNA polymerase regulator DksA.
Keywords: DnaJ; Salmonella; oxidation; redox signaling; stringent response.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
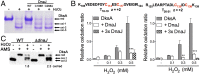
Comment in
-
Puzzling conformational changes affecting proteins binding to the RNA polymerase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 11;115(50):12550-12552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1818361115. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30498028 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

