Sustained activation of the Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor transcription factor promotes resistance to BRAF-inhibitors in melanoma
- PMID: 30429474
- PMCID: PMC6235830
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06951-2
Sustained activation of the Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor transcription factor promotes resistance to BRAF-inhibitors in melanoma
Abstract
BRAF inhibitors target the BRAF-V600E/K mutated kinase, the driver mutation found in 50% of cutaneous melanoma. They give unprecedented anti-tumor responses but acquisition of resistance ultimately limits their clinical benefit. The master regulators driving the expression of resistance-genes remain poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that the Aryl hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) transcription factor is constitutively activated in a subset of melanoma cells, promoting the dedifferentiation of melanoma cells and the expression of BRAFi-resistance genes. Typically, under BRAFi pressure, death of BRAFi-sensitive cells leads to an enrichment of a small subpopulation of AhR-activated and BRAFi-persister cells, responsible for relapse. Also, differentiated and BRAFi-sensitive cells can be redirected towards an AhR-dependent resistant program using AhR agonists. We thus identify Resveratrol, a clinically compatible AhR-antagonist that abrogates deleterious AhR sustained-activation. Combined with BRAFi, Resveratrol reduces the number of BRAFi-resistant cells and delays tumor growth. We thus propose AhR-impairment as a strategy to overcome melanoma resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
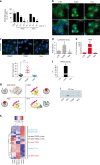

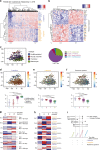

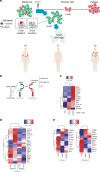

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

