Elevated ADAMTS13 Activity is Associated with Poor Postoperative Outcome in Patients Undergoing Liver Resection
- PMID: 30429491
- PMCID: PMC6235878
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34794-w
Elevated ADAMTS13 Activity is Associated with Poor Postoperative Outcome in Patients Undergoing Liver Resection
Abstract
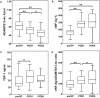
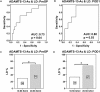
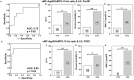
Recently, von-Willebrand-Factor (vWF) has been shown to correlate with postoperative liver dysfunction (LD). Accordingly, "disintegrin-like metalloprotease with thrombospondin type1 motif" (ADAMTS13) is known to cleave vWF in less active fragments. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the diagnostic potential of ADAMTS13-activity (ADAMTS13-AC) to identify patients with postoperative LD after hepatectomy. Accordingly 37 patients undergoing hepatectomy for different neoplastic entities were included in this study. Plasma ADAMTS13-AC and vWF-Ag were measured 1 day prior to (preOP), 1 and 5 days (POD1/5) after hepatectomy. In accordance to the ISGLS-criteria LD was prospectively recorded. In this context, perioperative ADAMTS13-AC- and vWF-Ag/ADAMTS13-AC-ratio- levels revealed a significant increase after hepatectomy. Accordingly, elevated vWF-Ag/ADAMTS13-AC-ratio significantly predicted LD (preOP AUC: 0.75, p = 0.02; POD1 AUC: 0.80, p = 0.03). Patients who fulfilled our perioperative vWF-Ag/ADAMTS13-AC-ratio cut-off-levels (preOP: ≥116, POD1: ≥165) suffered from significantly higher incidences of LD (preOP: 70% vs. 30%, p = 0.01; POD1: 83% vs. 17%, p = 0.001). In conclusion, perioperative ADAMTS13-AC measurement may serve as a useful parameter to early detect high-risk patients developing postoperative LD prior to liver resection in patients suffering from hepatic malignancies. Indeed, further investigations have to be performed to consolidate its role as a predictive marker for LD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

