Hypoxia-responsive lipid-poly-(hypoxic radiosensitized polyprodrug) nanoparticles for glioma chemo- and radiotherapy
- PMID: 30429888
- PMCID: PMC6217062
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.26225
Hypoxia-responsive lipid-poly-(hypoxic radiosensitized polyprodrug) nanoparticles for glioma chemo- and radiotherapy
Abstract
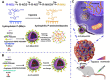
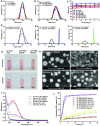
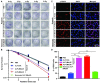
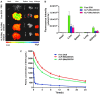
Treatment of malignant glioma is a challenge facing cancer therapy. In addition to surgery, and chemotherapy, radiotherapy (RT) is one of the most effective modalities of glioma treatment. However, there are two crucial challenges for RT facing malignant glioma therapy: first, gliomas are known to be resistant to radiation due to their intratumoral hypoxia; second, radiosensitizers may exhibit a lack of target specificity, which may cause a lower concentration of radiosensitizers in tumors and toxic side effects in normal tissues. Thus, novel angiopep-2-lipid-poly-(metronidazoles)n (ALP-(MIs)n) hypoxic radiosensitizer-polyprodrug nanoparticles (NPs) were designed to enhance the radiosensitizing effect on gliomas. Methods: In this study, different degrees and biodegradabilites of hypoxic radiosensitizer MIs-based polyprodrug (P-(MIs)n) were synthesized as a hydrophobic core. P-(MIs)n were mixed with DSPE-PEG2000, angiopep-2-DSPE-PEG2000 and lecithin to self-assemble ALP-(MIs)n through a single-step nanoprecipitation method. The ALP-(MIs)n encapsulate doxorubicin (DOX) (ALP-(MIs)n/DOX) and provoke the release of DOX under hypoxic conditions for glioma chemo- and radiotherapy. In vivo glioma targeting was tested in an orthotopic glioma using live animal fluorescence/bioluminescence imaging. The effect on sensitization to RT of ALP-(MIs)n and the combination of chemotherapy and RT of ALP-(MIs)n/DOX for glioma treatment were also investigated both in vitro and in vivo. Results: ALP-(MIs)n/DOX effectively accumulated in gliomas and could reach the hypoxic glioma site after systemic in vivo administration. These ALP-(MIs)n showed a significant radiosensitizing effect on gliomas and realized combination chemotherapy and RT for glioma treatment both in vitro and in vivo. Conclusions: In summary, we constructed a lipid-poly-(hypoxic radiosensitized polyprodrug) nanoparticles for enhancing the RT sensitivity of gliomas and achieving the combination of radiation and chemotherapy for gliomas.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; chemo- and radiotherapy; glioma; hypoxia-responsive; radiosensitized polyprodrug.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Self-assembled angiopep-2 modified lipid-poly (hypoxic radiosensitized polyprodrug) nanoparticles delivery TMZ for glioma synergistic TMZ and RT therapy.Drug Deliv. 2019 Dec;26(1):34-44. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2018.1534897. Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30744436 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a hypoxia-triggered and hypoxic radiosensitized liposome as a doxorubicin carrier to promote synergetic chemo-/radio-therapy for glioma.Biomaterials. 2017 Mar;121:130-143. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28088075
-
Hypoxia-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Nanoparticle-Combined Imaging-Guided Surgery and Multitherapy Strategies for Glioma.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Nov 25;12(47):52319-52328. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c12971. Epub 2020 Nov 9. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 33166112
-
Role of integrated cancer nanomedicine in overcoming drug resistance.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Nov;65(13-14):1784-802. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.07.012. Epub 2013 Jul 21. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23880506 Review.
-
Targeted and Non-Targeted Mechanisms for Killing Hypoxic Tumour Cells-Are There New Avenues for Treatment?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 11;22(16):8651. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168651. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Angiopep-2-Modified Nanoparticles for Brain-Directed Delivery of Therapeutics: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 12;14(4):712. doi: 10.3390/polym14040712. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The nanoprodrug of polytemozolomide combines with MGMT siRNA to enhance the effect of temozolomide in glioma.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):1-13. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2152911. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36579448 Free PMC article.
-
TH-302-loaded nanodrug reshapes the hypoxic tumour microenvironment and enhances PD-1 blockade efficacy in gastric cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 22;21(1):440. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02203-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37993847 Free PMC article.
-
Precise Construction of Dual-Promising Anticancer Drugs Associated with Gold Nanomaterials on Glioma Cancer Cells.Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2023 Oct 25;2023:8892099. doi: 10.1155/2023/8892099. eCollection 2023. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2023. PMID: 37920234 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Strategies for Nanoparticle-Based Radiosensitization in Glioblastoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 7;22(18):9673. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189673. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575840 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:492–507. - PubMed
-
- Sukhdeo K, Hambardzumyan D, Rich JN. Glioma development: where did it all go wrong? Cell. 2011;146:187–88. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ. et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96. - PubMed
-
- Bernsen HJ, Rijken PF, Peters H, Raleigh JA, Jeuken JW, Wesseling P. et al. Hypoxia in a human intracerebral glioma model. J Neurosurg. 2000;93:449–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

