Synthesis of dihydronaphthalene analogues inspired by combretastatin A-4 and their biological evaluation as anticancer agents
- PMID: 30429970
- PMCID: PMC6201230
- DOI: 10.1039/c8md00322j
Synthesis of dihydronaphthalene analogues inspired by combretastatin A-4 and their biological evaluation as anticancer agents
Abstract
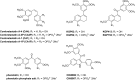
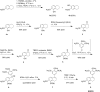
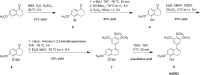
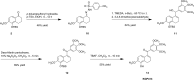
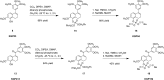
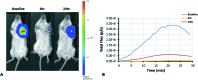
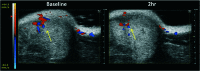
The natural products colchicine and combretastatin A-4 (CA4) have provided inspiration for the discovery and development of a wide array of derivatives and analogues that inhibit tubulin polymerization through a binding interaction at the colchicine site on β-tubulin. A water-soluble phosphate prodrug salt of CA4 (referred to as CA4P) has demonstrated the ability to selectively damage tumor-associated vasculature and ushered in a new class of developmental anticancer agents known as vascular disrupting agents (VDAs). Through a long-term program of structure activity relationship (SAR) driven inquiry, we discovered that the dihydronaphthalene molecular scaffold provided access to small-molecule inhibitors of tubulin polymerization. In particular, a dihydronaphthalene analogue bearing a pendant trimethoxy aryl ring (referred to as KGP03) and a similar aroyl ring (referred to as KGP413) were potent inhibitors of tubulin polymerization (IC50 = 1.0 and 1.2 μM, respectively) and displayed low nM cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines. In order to enhance water-solubility for in vivo evaluation, the corresponding phosphate prodrug salts (KGP04 and KGP152, respectively) were synthesized. In a preliminary in vivo study in a SCID-BALB/c mouse model bearing the human breast tumor MDA-MB-231-luc, a 99% reduction in signal was observed with bioluminescence imaging (BLI) 4 h after IP administration of KGP152 (200 mg kg-1) indicating reduced tumor blood flow. In a separate study, disruption of tumor-associated blood flow in a Fischer rat bearing an A549-luc human lung tumor was observed by color Doppler ultrasound following administration of KGP04 (15 mg kg-1).
Figures
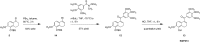
References
-
- Ludford R. J. JNCI, J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1945;6:89–101.
-
- Pettit G. R., Singh S. B., Hamel E., Lin C. M., Alberts D. S., Garcia-Kendal D. Experientia. 1989;45:209–211. - PubMed
-
- Pettit G. R., Singh S. B., Niven M. L., Hamel E., Schmidt J. M. J. Nat. Prod. 1987;50:119–131. - PubMed
-
- Pettit G. R., Singh S. B., Boyd M. R., Hamel E., Pettit R. K., Schmidt J. M., Hogan F. J. Med. Chem. 1995;38:1666–1672. - PubMed
-
- Pinney K., Pettit G., Trawick M., Jelinek C. and Chaplin D., in Anticancer Agents from Natural Products, Second Edition, CRC Press, 2011, pp. 27–64.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

