7-Deacetyl-10-alkylthiocolchicine derivatives - new compounds with potent anticancer and fungicidal activity
- PMID: 30429975
- PMCID: PMC6195099
- DOI: 10.1039/c8md00352a
7-Deacetyl-10-alkylthiocolchicine derivatives - new compounds with potent anticancer and fungicidal activity
Abstract
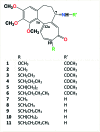
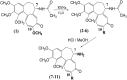
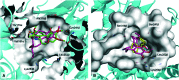
A series of new semi-synthetic 7-deacetyl-10-alkylthiocolchicne derivatives with ethyl, n-propyl, i-propyl and n-butyl substituents were synthesised and characterised by spectroscopic methods, elemental analysis, DFT calculations and molecular docking simulations. All the synthesized compounds have been tested for fungicidal and anticancer activities against SKOV-3, LoVo, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 and the lung-derived fibroblast CCD39Lu. All the new colchicine derivatives exhibit significantly higher cytotoxicity towards the SKOV-3 tumour cell line than the natural product - colchicine. The most effective cytotoxic agents were 7-deacetyl-10-n-buthylthiocolchicine and 7-deacetyl-10-i-propylthiocolchicine. Among all the compounds tested, 7-deacetyl-10-n-buthylthiocolchicine exhibited the highest fungicidal activity. Molecular modeling indicated that several mutations found in the β-tubulin unit of the tested fungal strains are crucial for antifungal activity and selectivity of 7-deacetyl-10-n-buthylthiocolchicine. The obtained results may be useful for the development of selective colchicine derivatives as effective fungicidal and/or anticancer drugs.
Figures
References
-
- Boyé O. and Brossi A., The Alkaloids, Chemistry and pharmacology, ed. A. Brossi and G. A. Cordell, Academic Press, New York, 1992, vol. 41, pp. 125–176.
-
- Brossi A. J. Med. Chem. 1990;33:2311–2314. - PubMed
-
- Zhang S. H., Feng J., Kuo S. C., Brossi A., Hamel E., Tropsha A., Lee K. H. J. Med. Chem. 2000;43:167–176. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

