Management of chronic hepatitis B during pregnancy
- PMID: 30430013
- PMCID: PMC6225824
- DOI: 10.1093/gastro/goy025
Management of chronic hepatitis B during pregnancy
Abstract
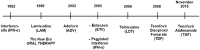
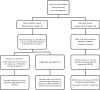
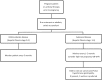
Chronic hepatitis B is globally prevalent and is a major cause of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Despite immunoprophylaxis against hepatitis B in pregnancy, perinatal transmission still occurs in at least 10% of the children born to a mother with high level of viremia. Decisions regarding hepatitis B therapy during pregnancy must take into account the benefits and safety for both the mother and the unborn baby. In this review, we summarize the current treatment options for chronic hepatitis B with a focus on management during pregnancy and the evidence-based strategies to prevent vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus (HBV).
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B; hepatitis B therapy; nucleoside analogue; pregnancy.
Figures
References
-
- Liu M, Li L, Zheng SJ et al. . Prevalence of major depression and its associations with demographic and clinical characteristics and quality of life in chinese patients with HBV-related liver diseases. Arch Psychiatr Nurs 2017;31:287–90. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. http://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ (March 2018, date last accessed).
-
- Welch S, Chiang B, Shadday P et al. . Estimated prevalence of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) in foreign-born (FB) persons living in the United States (US) by country/region of origin. Hepatology 2008;48(Suppl 1):687A–8A. - PubMed
-
- Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B: update 2009. Hepatology 2009;50:661–2. - PubMed
-
- Shi G, Zhang SX. Meta-analysis on the positive rate of hepatitis B surface antigen among pregnant women in China. Chin Prev Med 2013;1:26–30.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources