Biomechanical Behavior of an Implant System Using Polyether Ether Ketone Bar: Finite Element Analysis
- PMID: 30430073
- PMCID: PMC6187879
- DOI: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_183_18
Biomechanical Behavior of an Implant System Using Polyether Ether Ketone Bar: Finite Element Analysis
Abstract
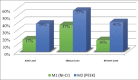
Aim and objectives: This study assessed, through finite element analysis, the biomechanical behavior of an implant system using the All-on-Four® technique with nickel-chromium (M1) and polyether ether ketone (PEEK) bars (M2).
Materials and methods: Implants and components were represented in three-dimensional (3D) geometric models and submitted to three types of load: axial, oblique, and load on all teeth. The 3D models were exported to a computer-aided design-like software such as Solidworks 2016 (Dassault Systemes, Solidworks Corps, USA) for editing and Nonuniform Rational Basis Splines parametrization.
Results: Data were analyzed according to system's areas of action: peri-implant bone, implant, intermediates, intermediates' screws, prostheses' screws, and bars. Largest peak stress was shown in M2.
Conclusion: PEEK is a promising material for use in dentistry; however, further studies are necessary to evaluate its performance.
Keywords: Biomedical and dental materials; dental implant-abutment design; dental implants; finite element analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Özdemir Doğan D, Polat NT, Polat S, Şeker E, Gül EB. Evaluation of “all-on-four” concept and alternative designs with 3D finite element analysis method. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2014;16:501–10. - PubMed
-
- Krekmanov L, Kahn M, Rangert B, Lindström H. Tilting of posterior mandibular and maxillary implants for improved prosthesis support. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000;15:405–14. - PubMed
-
- Calandriello R, Tomatis M. Simplified treatment of the atrophic posterior maxilla via immediate/early function and tilted implants: A prospective 1-year clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005;7(Suppl 1):S1–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

