Comparative analysis of the Sokal, Euro and European Treatment and Outcome Study score in prognostication of Indian chronic myeloid leukemia-chronic phase patients on imatinib
- PMID: 30430096
- PMCID: PMC6190386
- DOI: 10.4103/sajc.sajc_244_17
Comparative analysis of the Sokal, Euro and European Treatment and Outcome Study score in prognostication of Indian chronic myeloid leukemia-chronic phase patients on imatinib
Abstract
Introduction: The ultimate goal for CML management is risk stratification of the patients to design the appropriate treatment approach. The Sokal, Euro and EUTOS risk scores were established to prognosticate the patients on therapy.
Aim: To perform a comparative assessment of the Sokal, Euro and EUTOS prognostic score in Indian CML-CP patients on imatinib.
Methods: This is a retrospective study performed in 260 Ph+ CML-CP patients who were administered oral imatinib (400 mg/day).
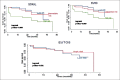
Results: 166/260 were males and 94/260 were females (M: F::1.6:1) with median age 35 years (range 20-70). 92 (35.38%), 125 (48.07%) and 43 (16.5%) patients were divided into low, intermediate and high risk Sokal score respectively. 102 (39.23%), 106 (40.76%) and 52 (20%) patients were discriminated into low, intermediate and high risk Euro score respectively. 210 (80.7%) and 50 (19.2%) patients were divided into low and high risk EUTOS score. Cumulative incidence of MMR for low, intermediate and high-risk Sokal score was 87%, 76% and 84% respectively (P = 0.016). Incidence of MMR in low, intermediate and high-risk Euro score was 93%, 85% and 68% respectively (P = 0.001). Incidence of MMR was 80 % and 81% for low and high risk EUTOS score (P = 0.764). Both EFS and OS are significantly correlated with Sokal score (P = 0.004, P = 0.007) and Euro score (P = 0.009, P = 0.001) but not with EUTOS score (P = 0.581, P = 0.927).
Conclusion: The present study highlights the significant prognostic role of Sokal and Euro score in predicting the treatment outcome of the CML- CP patients on imatinib.
Keywords: Chronic myeloid leukemia-chronic phase; Euro; European Treatment and Outcome Study; Sokal; imatinib; prognostication.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Three Prognostic Scoring Systems in Predicting the Response and Outcome in Pediatric Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Chronic Phase on Frontline Imatinib.Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2017 Jul-Sep;38(3):282-286. doi: 10.4103/ijmpo.ijmpo_104_16. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29200674 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Sokal and Eutos Scores for Predicting Cytogenetic and Molecular Response in Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia-Chronic Phase Patients on Imatinib.Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2017 Mar;33(1):82-86. doi: 10.1007/s12288-016-0667-x. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2017. PMID: 28194061 Free PMC article.
-
EUTOS CML prognostic scoring system predicts ELN-based 'event-free survival' better than Euro/Hasford and Sokal systems in CML patients receiving front-line imatinib mesylate.Hematology. 2013 Sep;18(5):247-52. doi: 10.1179/1607845412Y.0000000071. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Hematology. 2013. PMID: 23540886
-
Prognostic scores for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia under particular consideration of competing causes of death.Ann Hematol. 2015 Apr;94 Suppl 2:S209-18. doi: 10.1007/s00277-015-2316-0. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Ann Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25814087 Review.
-
First-line treatment of newly diagnosed elderly patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: current and emerging strategies.Drugs. 2014 Apr;74(6):627-43. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0207-7. Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24711014 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Prognosis and Therapy: Criticisms and Perspectives.J Clin Med. 2020 Jun 2;9(6):1709. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061709. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32498406 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Can We Identify Prognostic Factors?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 19;13(16):4175. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164175. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Trask PC, Mitra D, Iyer S, Candrilli SD, Kaye JA. Patterns and prognostic indicators of response to CML treatment in a multi-country medical record review study. Int J Hematol. 2012;95:535–44. - PubMed
-
- Verbeek W, König H, Boehm J, Kohl D, Lange C, Heuer T, et al. Continuous complete hematological and cytogenetic remission with molecular minimal residual disease 9 years after discontinuation of interferon-alpha in a patient with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Acta Haematol. 2006;115:109–12. - PubMed
-
- Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, O’Brien S, Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM, et al. The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:164–72. - PubMed
-
- Cwynarski K, Roberts IA, Iacobelli S, van Biezen A, Brand R, Devergie A, et al. Stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in children. Blood. 2003;102:1224–31. - PubMed
-
- Sokal JE, Cox EB, Baccarani M, Tura S, Gomez GA, Robertson JE, et al. Prognostic discrimination in “good-risk” chronic granulocytic leukemia. Blood. 1984;63:789–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

